Content
- 1 Description of the chayote plant with photo
- 2 Chayote varieties
- 3 Chemical composition and calorie content of chayote
- 4 Benefits of chayote
- 5 How to eat chayote
- 6 Medicinal use
- 7 Contraindications for use
- 8 How to Grow Chayote
- 9 Diseases and pests of chayote
- 10 Propagation of chayote (Mexican cucumber)
- 11 Harvesting and storage
- 12 Conclusion
Chayote is a perennial vegetable crop, popularly called the Mexican cucumber. The exotic plant is very demanding of heat. Outside the southern regions, it can only be grown in a greenhouse using seedlings.
Description of the chayote plant with photo
Chayote came to Europe from Central America. For the first time in Russia, it began to be cultivated on the Black Sea coast in the 50s of the twentieth century.
The Mexican cucumber belongs to the Cucurbitaceae family. It can grow in one place for up to 25 years. During this time, its vines stretch up to 25-30 m. Over time, the chayote stem becomes woody.
The leaves of the Mexican cucumber are large and attached to the vine by cuttings. Flowering begins in June, the inflorescences are small. Both female and male flowers are formed on one bush at the same time. Chayote fruits are shaped like a pear and are yellow or light green in color. The skin is smooth, like a pumpkin, and may have grooves.
The weight of the fruit varies from 300 to 900 g.The length of the berry reaches from 8 to 20 cm, in diameter 7-12 cm. The fruit is ready for consumption about a month after pollination of the flower.
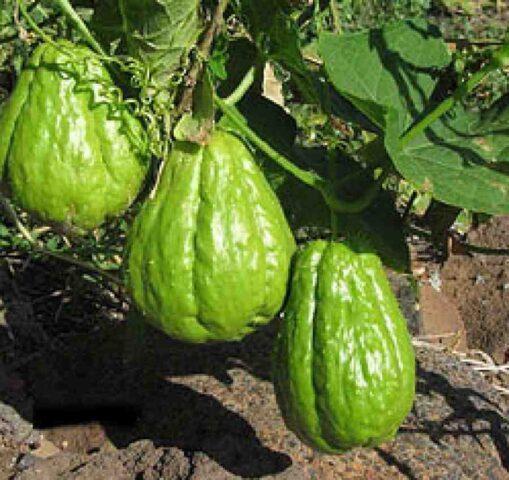

Each fruit contains one large seed.
Chayote tastes vaguely like zucchini. You can eat not only berries. Tubers weighing from 200 g to 1 kg are formed on the root of the Mexican cucumber. They taste almost no different from potatoes and are similar in color to fruits on a vine. Up to 50 kg of tubers are collected from each bush.
Chayote varieties
There are 12 varieties of chayote in nature, only three of which are popular among Russian gardeners. French - the surface of the fruit is covered with furrows and thorns, the berry is colored green. White - Chayote has a smooth skin. Cream-colored surface. The green variety is characterized by smooth skin.
The fruits of the Mexican cucumber can be spherical, conical, pear-shaped or oval-elongated.
Chemical composition and calorie content of chayote
Chayote is considered a dietary product. Calorie content 119 kcal per 100 g. The composition includes useful substances.
Vitamins | % ratio per 100 g of product | Minerals | % ratio per 100 g of product |
IN1 | 1,7 | Calcium | 1,7 |
IN2 | 1,6 | Magnesium | 3 |
IN5 | 5 | Phosphorus | 2,3 |
IN6 | 3,8 | Iron | 1,9 |
IN9 | 23 | Manganese | 9,5 |
WITH | 8,6 | Copper | 12 |
E | 0,8 | Zinc | 6,2 |
TO | 3,4 | Potassium | 5 |
RR | 2,4 | Selenium | 0,4 |
Kholin | 1,8 |
|
|
Carbohydrates predominate in Mexican cucumber - 73%. Protein content – 21%, fat – 6%.
Benefits of chayote
Chayote fruits are good for health.
Pros of Mexican cucumber:
- helps in the treatment of diseases of the mammary and thyroid glands, helps cleanse the blood;
- a decoction of Mexican cucumber leaves effectively fights swelling;
- The low calorie content of the product promotes weight loss. Chayote is indicated for use in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hemorrhoids, fibroids;
- vitamins and microelements included in the culture increase the protective properties of the body.

Chayote is rich in amino acids that stimulate the brain and nervous system.
How to eat chayote
In the Mexican cucumber, only the stem of the plant is inedible. All other parts of the culture can be eaten:
- Boiled cucumber fruits are combined with any vegetables. Chayote can be used to make puree, stew, or add to soup. Mexican cucumber is baked in the oven, stuffed, and preserved for the winter. Also, the fruits of the plant can be consumed fresh, after salting them (this way the body will absorb more vitamins).
- The tubers of the plant are rich in starch. After drying, they are ground into flour, which is used to prepare dietary dishes. Fried tubers taste like potatoes.
- Green chayote leaves are added to summer salads.
Medicinal use
In folk medicine, tubers, leaves and fruits of chayote are used. The pulp of the Mexican cucumber has a laxative effect and helps relieve constipation. Decoctions from the tubers of the plant reduce blood pressure and are used to treat atherosclerosis.
Contraindications for use
Before preparing Mexican chayote cucumber, you need to know about the benefits and harms of the exotic. It is not recommended to eat it on an empty stomach. The vegetable irritates the mucous membrane and provokes colic.
In what cases is it contraindicated to use Mexican cucumber:
- renal dysfunction associated with edema;
- increased acidity of gastric juice. Chayote will only aggravate the process, causing weakness and nausea.
For gastritis, you can eat vegetables that have undergone heat treatment.It is acceptable to include fresh produce in the diet in limited quantities. Chayote stored for the winter causes cramps.
Another contraindication is individual intolerance.
How to Grow Chayote
In open ground, it is not recommended to grow chayote in beds where pumpkins used to grow. Onions, potatoes, and cabbage are considered the best predecessors.

Before planting an exotic cucumber in the ground, the soil should be fertilized with rotted manure
How to plant chayote
Growing Mexican chayote cucumber at home is possible from seedlings. Planted in late February or early March. To do this, use a large container, since 2/3 of the fruit should be placed in the ground. The vegetable, at an angle of 45ᵒ, is buried into the soil with its wide part.
Chayote care
Transplantation to a permanent location is carried out in mid-May in warm soil. When cultivating in open ground, the area should be illuminated by sunlight and protected from gusts of wind. A draft can completely destroy the crop, since cucumbers are attached to the vine with a relatively thin petiole. The root does not tolerate stagnant water, so care should be taken to ensure drainage. If there is a threat of night frosts, the seedlings are first covered with film at night.
Since the plant grows 10-20 m high, you should prepare a trellis in advance or direct the cucumber to weave along a tree or along an arch.
Rules of care:
- Watering is carried out at least once every 10 days.In the greenhouse, the procedure should be carried out twice during this period. At least 10 liters of warm, settled water are poured under the bush (the temperature of the liquid should not be lower than +25ᵒC). Excess moisture will negatively affect crop growth.
- When the soil is shaken after irrigation so that a crust does not form, the soil around the cucumber root is loosened and the weeds are removed. When the bush reaches a height of 70-80 cm, it is hilled.
- The trunk is led into 2-3 shoots, the remaining branches are branched, repeating the procedure every few weeks.
- During the growing season, the cucumber should be fed 3-4 times, alternating organic and mineral fertilizers.
In open ground, the plant rarely manages to overwinter safely. Most often, the roots become wet, after which the plant dies. But in the southern regions, where winters are not so severe, you can try to preserve the bush by insulating the root circle with sawdust or straw. In greenhouses, even if they are not heated, cucumbers overwinter well.
Diseases and pests of chayote
Exotic culture is affected by the same ailments as the usual variety. Fruit quality and yield are affected by viruses, bacteria, fungal spores, and pests. If measures are not taken to combat them, the plant may die completely.
During cultivation in open ground, the seedling is affected by:
- powdery and downy mildew;
- gray and white rot;
- macrosporiosis;
- anthracnose
If a plant lacks nutritional components, it may suffer from infectious diseases.
Pests attacking exotic cucumber: wireworm, melon aphid, whitefly, thrips, root-knot nematode, spider mite, cutworm.
It is recommended to fight parasites and diseases in the early stages.
Pests are controlled with biological products and insecticides
Chemicals and folk remedies are used to treat diseases. Chayote is a delicate vegetable; compliance with the instructions and consumption rates is mandatory.
Propagation of chayote (Mexican cucumber)
The most convenient and effective way to propagate the population is to grow chayote from the fruit by planting the whole vegetable in the ground. A variant of vegetative propagation is also practiced, when cuttings 15-20 cm long are cut from young shoots. They are planted under film covers.
A less common way to plant chayote is directly with seeds extracted from the fruit.
Harvesting and storage
The Mexican cucumber is harvested in September. The fruits are carefully removed, being careful not to damage them. If the integrity of the skin is compromised, they will not last long. The harvest must be immediately processed. It is also not recommended to store fruits of non-standard shape; they will begin to deteriorate first, contaminating other vegetables. Then it will not be possible to save the chayote for planting.
Whole cucumbers are placed in wooden boxes. Store in a dry, dark place. Before lowering the crop into the basement, the stalks are removed and the fruits are dried. Under favorable conditions, chayote can be preserved until spring (the average period is six months).

Up to 80 kg of cucumbers are harvested from each bush per season
Conclusion
Chayote is a low-calorie exotic vegetable rich in microelements and vitamins. Mexican cucumber provides the body with the daily requirement of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The agricultural technology for growing the crop cannot be called easy, but the yield per bush is 80 kg, which fully covers the costs.








