Content
Walnut diseases occur due to an incorrectly selected planting location or insufficient care. The crop is hardy, with good immunity, and is affected less frequently than fruit trees.
Basics of proper tree care
Walnut is a tree that grows in almost every garden. His life expectancy is long. There are specimens that bear fruit for 400 years. To prevent the appearance of diseases and pests, you need to approach planting wisely and properly care for walnuts:
- The soil at the planting site must be fertile. It is dug up with humus or compost.
- The groundwater level should not be high. The planting pit must be drained.
- Choose a place in the sun. The tree does not tolerate shading and may die.
- After planting, the root collar of the walnut should be level with the soil.
Planting begins in early spring; nuts can be planted in the fall only in the southern regions. The seedling manages to take root before the first frost.
Complete walnut care consists of several points:
- pruning;
- whitewash;
- watering;
- feeding;
- organization of wintering.
Pruning begins in the spring, when the temperature rises to +4... +5°C. All shoots that thicken the crown and interfere with its good ventilation are cut out. After this, dry and poorly overwintered branches are removed. The procedure is completed by whitewashing the trunk and skeletal branches. Old bark, lichens or growths are first removed. The barrel is treated with a solution of copper sulfate, after which it is thoroughly whitened.
It is no secret to an experienced gardener that walnuts need abundant watering, especially if the weather is dry. The soil is moistened to the entire depth of the roots. During periods of extreme heat, water the tree 2 or 3 times a month. At the same time, 3-4 buckets of water are consumed per plant.
The seedling can be fertilized 3 years after planting. If the planting pit was filled according to all the rules, then the feeding will be enough for this entire period. In spring and autumn, ammonium nitrate is applied, in the summer they switch to fertilizing containing phosphorus and potassium.
Adult nuts overwinter well without additional shelter, but young seedlings must be insulated before the onset of cold weather. The tree trunk circle is mulched with humus to a height of 10 cm.
Walnut diseases and their control
There are a lot of diseases in walnuts, some dangerous and some not so dangerous. The duration of fruiting depends on proper treatment. To correctly diagnose the disease, you need to carefully examine the trunk, leaves and buds of the tree.
Bacteriosis
Bacteriosis is an infectious disease of walnuts that affects almost all its parts.It appears as black spots on the leaves, after which they completely dry out and fall off. Young shoots are also covered with brown dots.
The disease spreads during the flowering period, and some of the flowers and ovaries suffer. After which the wood and green shoots die off. The pathogen overwinters in the buds, under the bark and in fallen leaves. In spring, the infection spreads to healthy parts of the walnut through frost holes. Rainy weather especially contributes to this.
For the treatment and prevention of bacteriosis, a 3% solution of Bordeaux mixture and a 1% urea mixture are used. Treatments are planned 14 days after flowering.
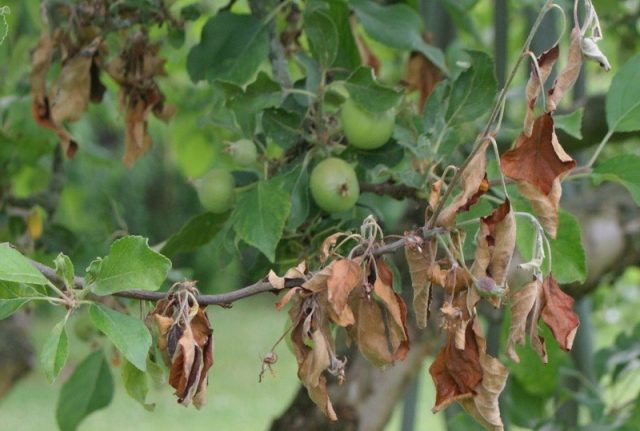
Bacterial burn
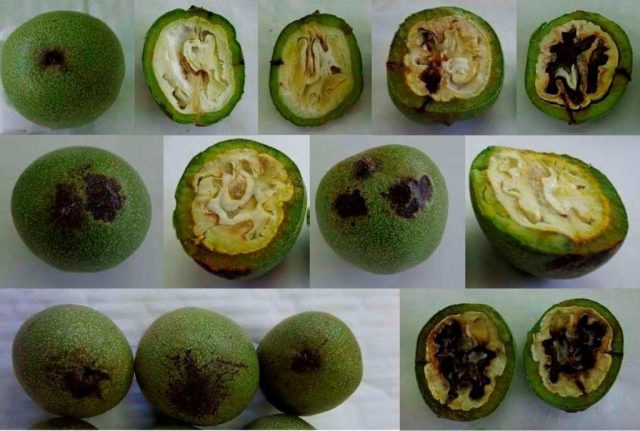
Fire blight is one of the worst tree diseases. It appears on leaves, young shoots, and affects flowers. Walnut leaves become covered with watery black spots; they dry out but do not fall off. Buds and young shoots die off completely, and ulcers appear on the trunk and branches. The skin of the fruit becomes stained and the kernel turns completely black.
The disease spreads rapidly, especially during the rainy season. Carried by pollen and insects.
To combat bacterial burns, preparations containing copper are used. As a preventive measure, treatments are carried out several times in a row:
- in spring, before flowering;
- in autumn, after harvest.
You can use "Zineb" or "HOM". Spraying is carried out in dry, windless weather.
White spot
This disease is quite rare. The causative agent is a fungus that settles on the inside of the leaf.The affected plates become covered with light green spots with a white coating. White spotting develops in cold and damp weather.
To combat the disease, 1% Bordeaux mixture is used. Most often, walnuts are affected in nurseries where the plantings are too dense.
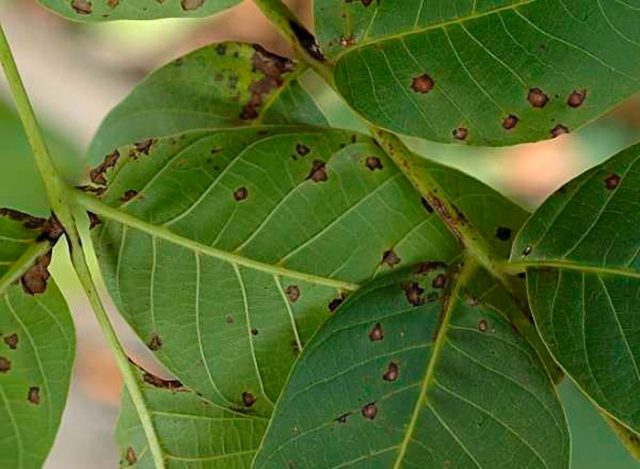
Brown spot (phyllostictosis)
The fungal disease manifests itself as yellow-brown spots on nut leaves, which lead to tissue necrosis. Dry leaves die, shoot growth slows down, and the plant's frost resistance is significantly reduced. It is difficult to destroy the fungus; the pathogen overwinters in plant debris and under the bark. In rainy spring, spores are spread to healthy tissues and the disease progresses again.
To get rid of brown spot, walnuts are treated with copper oxychloride or a 1% solution of Bordeaux mixture. Spraying is carried out until complete cure.
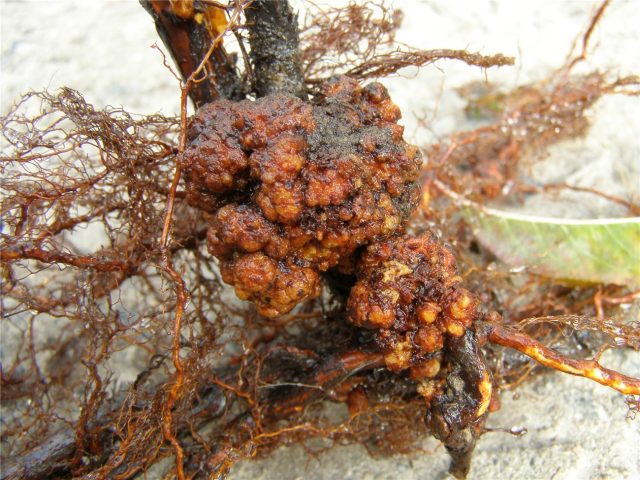
Root cancer
The disease affects the root system of young seedlings and adult nuts. It manifests itself as growths on the roots, as a result of which the fruiting of the crop decreases or completely stops, winter hardiness worsens, and growth slows down. In advanced cases, the plant dies.
The walnut disease that can be seen in the photo is not easy to detect. It is possible to accurately diagnose root cancer only after digging up a seedling.
The causative agent of the disease enters the roots through frost holes, cracks in the bark or other damage. That is why the trunk and skeletal branches of the tree need careful care.In spring and autumn, all growths, cracks and damaged areas are cleaned to healthy tissue and treated with copper preparations, caustic soda solution, after which they are covered with garden varnish and whitewashed.
Marsonia
The disease appears on walnut leaves as brown dots, which gradually grow and occupy the entire surface of the leaf blade. As a result, leaf fall begins earlier than usual. In addition, unripe fruits that have been affected by marsoniosis also fall off. Productivity drops sharply.
At the first signs of disease, leaves are removed from the affected tree, and the crown is treated with copper-containing preparations. Marsonia spreads in rainy weather. If there is little precipitation, the cause may be waterlogging of the soil as a result of improper watering. The regime should be reconsidered, otherwise the whole tree will suffer.
To prevent the disease in the spring, the nut is sprayed with the drug “Strobi”, which is diluted according to the instructions. The treatment is done before the buds open. In the summer, the Vectra will save you from illness.
Walnut pests and their control
A tree weakened by disease is more often attacked by pests, which are not always easy to get rid of quickly. To achieve a lasting result, several treatments are necessary.
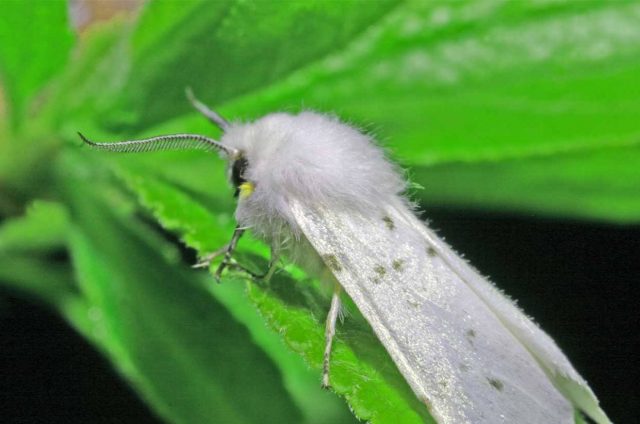
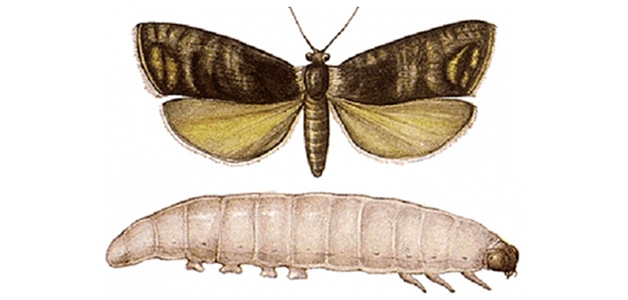
American white butterfly
The most common and dangerous pest of walnuts. The butterfly is white, sometimes it has black or brown spots on its wings. One individual lays up to 1,500 eggs per season, the third brood is especially dangerous. Caterpillars pupate and overwinter on the soil surface, under leaves, in tree bark, and in cracks in the trunk.With the arrival of spring, they begin to cause harm again.
In one season, the insect produces several generations, so a single spraying does not give anything. The butterfly lays caterpillars on the leaves and young shoots of the nut. The voracious young growth quickly eats them and spreads throughout the tree.
In the fight against insects, it is important to destroy the first generation, as the rest cause even more harm. The nut is examined, the caterpillar nests are removed and destroyed. The procedure is repeated every week. The most effective remedy against butterflies is the microbiological preparation “Lepidocide”. Treatment is carried out before and after walnut flowering.
King nut moth
The pest lays eggs in nut leaves. The lesion can be determined by the presence of dark tubercles on the surface of the leaf blade. Walnut moth caterpillars feed on the cell sap of leaves, eating away the pulp from the inside. In case of severe damage, the tree is treated with pesticides:
- "Decamethrin";
- "Decis".
The drugs are diluted according to the instructions, treatments are repeated every 15-25 days.
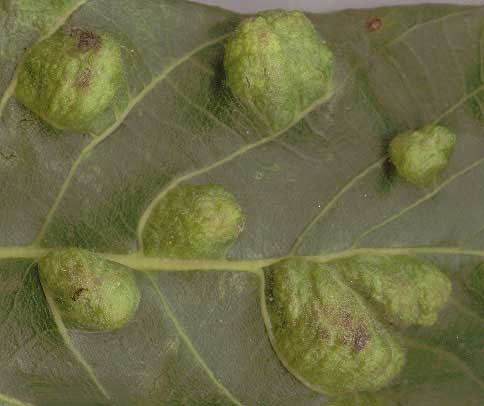
Walnut warty (gall) mite
Fungal diseases of walnuts lead to damage to the tree by gall mites, which attack it during periods of high air humidity. The pest feeds on young foliage and does not harm fruits. Its presence can be determined by characteristic signs:
- dark brown tubercles appear on the leaves;
- the growth of young shoots slows down;
- the leaf plate spontaneously dries and curls;
- a thin cobweb is visible on the reverse side of the leaf.
Acaricides such as “Aktara” and “Akarin” are used against ticks. Spray the nut several times with an interval of 15 days.
Sapwood
The pest settles on a weakened plant.It is simply impossible to notice its presence at the initial stage, since it climbs under the bark. Gradually, the beetle gnaws out passages near the buds and eats them. The tree begins to produce gum.
You can protect the walnut from the sapwood. In spring and autumn, be sure to prune the crown, cutting out dry and affected shoots. For prevention purposes, the tree is sprayed with insecticides.
codling moth
The pest is dangerous for the fruit, as it eats out the nut kernels, significantly reducing the yield. Damaged fruits fall prematurely. One caterpillar eats 2-3 nuts. Peak pest activity occurs between May and September.
You can catch the codling moth mechanically. To do this, traps with pheromones are used, which catch males. They are removed and destroyed, which significantly reduces the number of offspring. If the tree is severely damaged, drugs with viruses are used that cause inflammation of the granulomas in the pest.
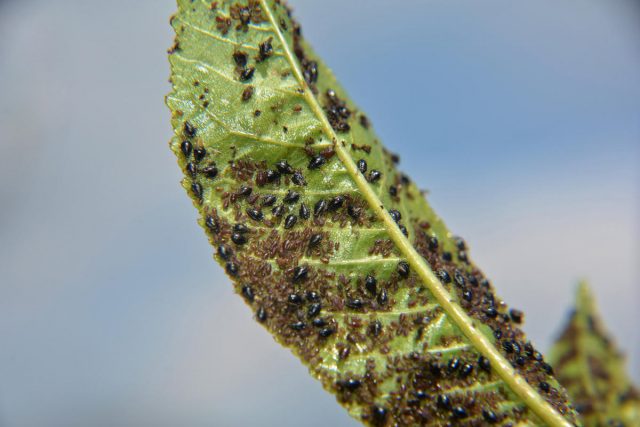
Aphid
The pest settles on the underside of the leaf blade and sucks the juice from the tissues. As a result, the leaves curl, die and fall off. The nut quickly weakens and slows growth. The fruits do not have time to ripen at the right time and also fall off.
Aphid infestations can be observed after rain. First of all, young leaves are affected, which leads to their diseases. At this time, the walnut is sprayed with “Karate” or “Decis” preparations. Treatments should not be carried out during flowering, so as not to destroy the bees. The interval between spraying is 15-25 days. After rain, treatments are repeated.
Prevention of walnut diseases
To prevent diseases and pests of walnuts, it is important to properly care for the plant. Particular attention is paid to the tree in spring and autumn.
In early spring, the soil under the nut is loosened and granular mineral fertilizers are spread to increase the plant’s immunity to diseases. Pruning is mandatory. Before buds open, preventive treatments are carried out with complex preparations against various diseases and pests.
In summer, the tree trunk area is kept clean by promptly removing weedsto prevent pests from breeding in them. After all, they are the ones who transmit various fungi and viruses to the plant.
In the fall, the nut is trimmed again, after which the crown is sprayed with approved preparations for prevention. Before frost, all fallen leaves, fruits and plant debris are removed to reduce the number of wintering pests. When the outside temperature reaches a stable subzero temperature, the soil under the nut is dug up. Some of the pupated pests will die. To increase the tree’s immunity and winter hardiness, experienced summer residents advise carrying out late water-recharging watering. It is planned for the end of autumn, before the frosts have yet begun.
Conclusion
Walnut diseases lead to significant yield loss, so their occurrence should be prevented. To do this, the tree is not left unattended for a long time and is grown in accordance with the recommendations of experienced gardeners.


















How to treat tall walnut?