Content
Propagation of fruit trees and shrubs by grafting among summer residents is considered “aerobatics”: this method is subject to only the most experienced gardeners with extensive experience. But even beginners really want to get some rare and expensive variety for their garden, but it is not possible to buy a real seedling. In this case, a method of grafting fruit trees such as budding will be useful. The most important advantage of this method is the high percentage of plant survival. Budding can be carried out even in unfavorable weather conditions, and to carry it out you only need one bud of the desired crop.
This article is about the effectiveness of budding fruit trees and shrubs, the advantages of this grafting method and the technology for its implementation.
What it is
The first thing a novice gardener who decides to start propagating his trees will encounter is terminology. To begin with, a beginner only needs to master two terms: rootstock and scion. In this case, rootstock They call the plant on the roots or other parts of which a new species will take root. Scion same - this is part of the tree that the gardener would like to propagate and have on his own plot.
Today, at least two hundred methods of grafting fruit trees and berry bushes are known. And budding is considered one of the simplest.
Budding is the grafting of a plant with one bud or one eye. The methods of such vaccination differ in the technology of implementation, which can be individual for each summer resident.
A bud is taken from a cultivated plant that needs to be propagated. It can be grafted onto any rootstock, be it a wild one or a varietal tree. Budding may differ in execution time, divided into summer and spring:
- In the spring, trees are propagated by a bud that formed last summer. Cuttings with such buds should be cut at the end of winter or autumn and stored in a cool, dark place (in the basement, for example). Such a bud will begin to grow already in the current season, so the grafting method is called budding with a germinating eye.
- For summer budding takes a bud that has matured this season. The grafting material (eye) is cut out immediately before transplantation. The eye grafted in summer should take root, overwinter and begin to grow only next spring. Therefore, the method of vaccination is called budding with a sleeping eye.
Advantages of grafting trees with buds
Grafting fruit trees using the budding method has clear advantages:
- ease of vaccination, accessible even to a beginner;
- minor injury to the rootstock and propagated plant;
- minimum amount of scion material - just one eye;
- execution speed;
- the possibility of repeating the grafting on the same area of the tree if the procedure is unsuccessful;
- good kidney survival rate - most often the vaccination is successful;
- compatibility of varietal crops with wildflowers and any other rootstocks;
- Possibility of vaccination twice a year.
It is very important to follow the recommended timing for budding and cutting cuttings. It is at this time that the bark easily peels off from the tree, and the eye can be cut off without traumatizing the shoot. Intensive division of cambium cells during the same period ensures good survival of the scion and guarantees excellent results.
Execution technology
Budding of fruit trees can be done in a variety of different ways. Any summer resident can even develop his own eye grafting technology. Below we will consider a couple of the most popular and “win-win” budding options.
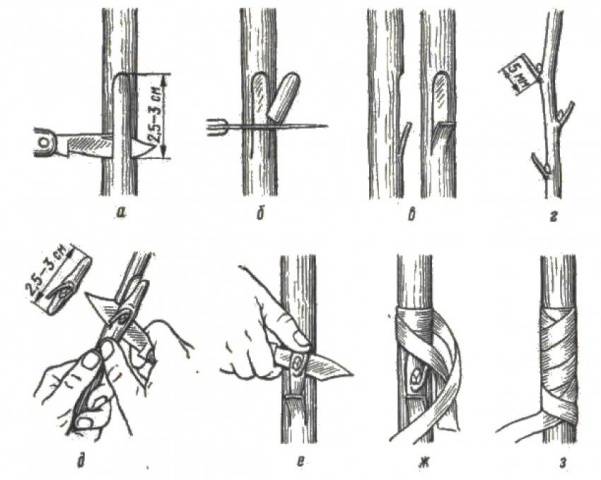
Grafting eyes into the butt
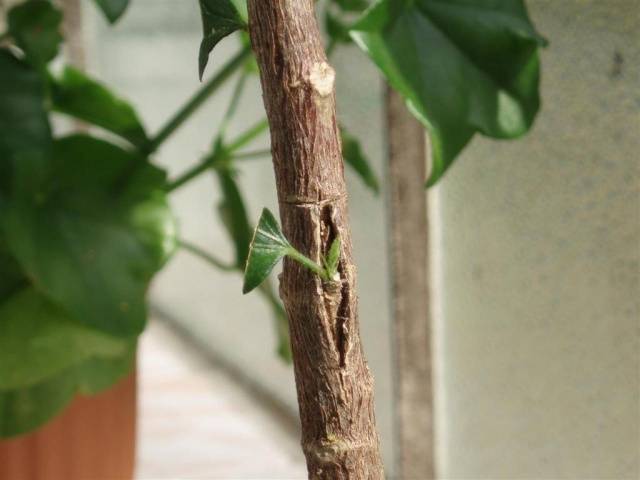
The simplest and fastest method of budding, which consists of applying a cut section of bark with a bud to the same cut on the rootstock.
The grafting of the eye into the butt should be done as follows:
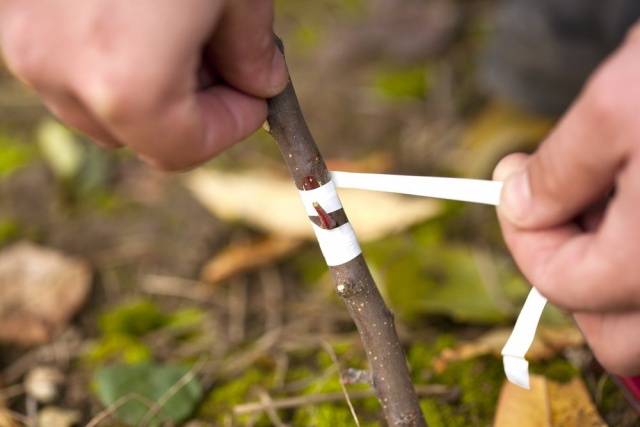
- Prepare the necessary tools: a sharp knife with a thin blade, winding tape.
- Wipe the rootstock area with a damp cloth to remove dust and dirt.
- With a knife you need to cut along the rootstock to a depth of 2-2.5 cm, making a “tongue”.Less than half of the resulting “tongue” must be cut off.
- From a cutting of a valuable variety, you should cut out a shield with a bud of the same size (2-2.5 cm) and shape.
- The shield is brought behind the “tongue”, aligning its edges with the cutout on the bark of the rootstock. If the shield protrudes beyond the edge, it is trimmed with a knife. When the scion is narrower than the cut, at least one of its edges is connected to the cut on the rootstock.
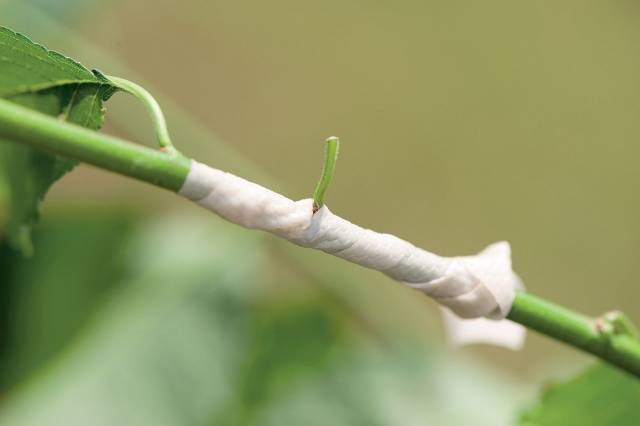
- The grafting site is tightly bandaged with polyethylene or special budding tape. The bud itself can be either bandaged or left outside - gardeners have differing opinions on this matter, but practice proves the viability of any of the wrapping methods.
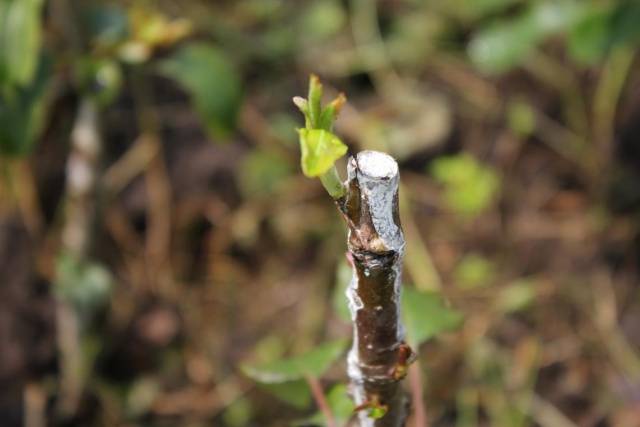
- After two weeks, the vaccine should take root.
In this case, the thickness of the rootstock is not significant, so the eyes can be budded on overgrown shoots. Another advantage of the butt method is the slight dependence of the success of the event on the time of year: you can engage in budding from mid-June until the last days of summer.
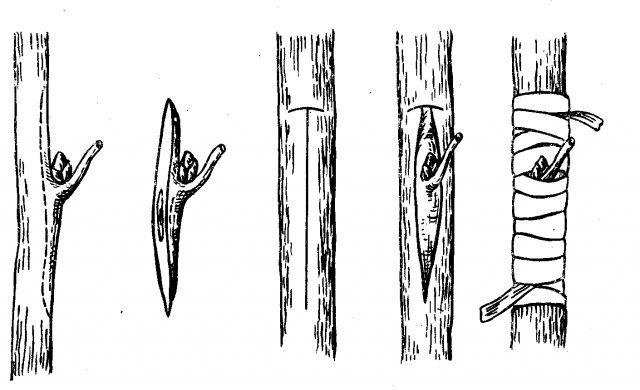
Vaccination with a shield in a T-shaped neckline
The essence of such budding is to grind the bud to the cambium layer in the rootstock through a cut in the bark. It is very important to choose the right moment here: the sap flow in the tree at the time of grafting should be the most intense.
Performing budding in a section is very simple:
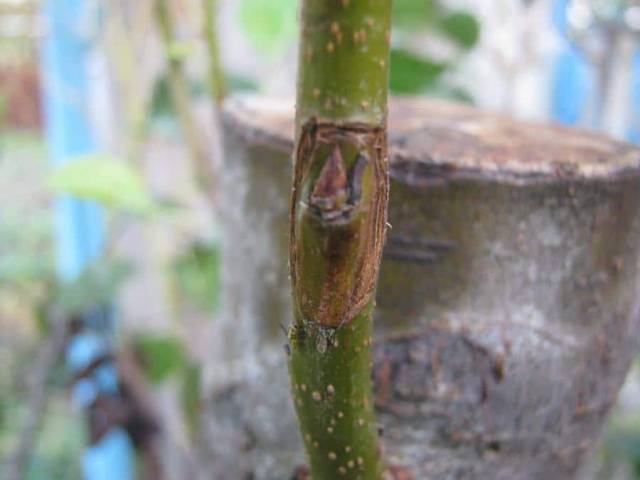
- From a varietal cutting you need to cut out a bud along with a rectangular or oval section of bark: about 2.5-3 cm long and 0.5 cm wide. The thickness of the shield should be small.
- A T-shaped cut is made in the bark of the rootstock, the dimensions of which correspond to the dimensions of the scion.First a horizontal incision is made, then a vertical incision. After this, the edges of the vertical cut are slightly bent to form a “pocket” for the shield with the scion.
- A scion with an eye is inserted into the “pocket” from top to bottom. The upper edge of the shield is adjusted with a knife so that the edges of the scion and rootstock bark fit tightly to each other.
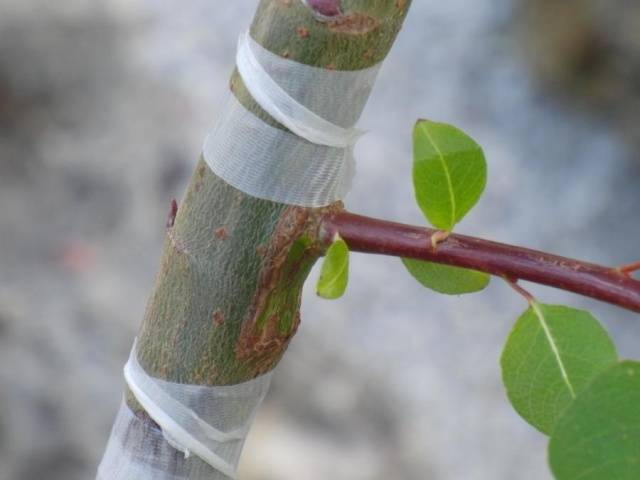
- The shield is tightly bandaged to the rootstock with plastic tape or electrical tape. They start bandaging from the bottom, and it is better to leave the kidney open.
- With spring grafting, the bud should grow in 15 days. The success of the summer event is indicated by the easy separation of the petiole located above the bud.
Secrets of success
For the vaccination to be successful, some requirements must be met:
- choose young shoots for budding whose diameter does not exceed 10-11 mm;
- the bark on the knot should be smooth and elastic;
- you should not plant an eye on the southern side of the crown - the sun will dry out the rootstock area;
- for guaranteed success, you can graft two buds at once on both sides of the rootstock, but they should be tied at the same time;
- To perform the method, no putty is required; polyethylene is sufficient;
- on one shoot you can plant several eyes in a row, only the interval between them should be 15-20 cm;
- the lower bud should be grafted at least 20-25 cm from the fork of the trunk;
- It is strictly not recommended to breed in rainy weather;
- In summer, for grafting, choose a cloudy, cool day or do budding in the morning or evening;
- a couple of weeks before the summer grafting, it is recommended to water the tree to activate the sap flow process in it;
- Fully mature, large eyes located in the middle part of the shoot take root best;
- Only well-ripened cuttings are suitable for bud grafting, which can be recognized by the characteristic cracking sound when bending.
Conclusion
Budding is the simplest and most affordable way to graft fruit trees and shrubs. Inexperienced gardeners are recommended to start with this method of propagation, because the trauma to the rootstock in this case will be minimal. If the bud does not take root, the procedure can be easily repeated and the same shoot can be used.
More information about budding fruit trees is described in this video: