Content
Apricot Honey is distinguished by dense, numerous and sweet fruits. The tree is unpretentious in care, easily takes root in all regions, and is characterized by increased winter hardiness and drought resistance. The variety was bred for cultivation in the northern regions. Its productivity is high, the fruits are suitable for fresh consumption and processing.
History of selection
The honey apricot variety was developed in 1996; it is still not included in the Russian state register. Breeders from the Yuzhnouralsk Research Institute of Horticulture and Potato Growing worked on a new fruit tree. Scientists tried to obtain a winter-hardy apricot. As a result of free pollination of the Kichiginsky variety, a new type of fruit appeared.
The frost-resistant tree takes root well in the Urals and Siberia. For this purpose, K.K. Mulayanova carried out work so that gardeners in the northern regions could enjoy sweet fruits.
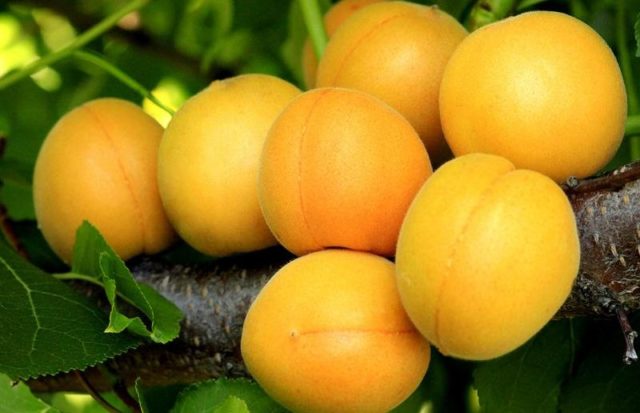

Honey apricot fruits are all the same shape and size, they are suitable for sale
Description of the Honey apricot variety
The fruits of the Honey Apricot are small in size, weighing up to 15 g, yellow in color, with small red spots. When cut, the fruit is the same color as the peel, the pulp is of medium density. The stone is easily separated, has an almond shape, and is colored brown. Fruit tasting score: 4.3. They attract with their honey taste.
The tree reaches a height of 4 m, the crown is spreading, triangular in shape. The foliage is light green in color. The peduncles are painted burgundy, the bark is rich brown. Fruiting begins in the fifth year of the growing season; 20-30 kg of fruit are harvested from one apricot.
Characteristics of apricot Honey
A description of honey apricot is presented in the video below. Before purchasing a tree, it is advisable to study all the characteristics in advance in order to comply with the rules of agricultural technology.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
Honey apricot can tolerate frosts down to -40 0C. Such features appear closer to the third year of the growing season. Until this age, it is advisable to cover the planting for the winter. This tree easily tolerates spring frosts, unlike other fruit and berry crops.
The fruit plant also tolerates heat. However, do not forget about timely watering. If you plant a tree near groundwater, it will independently receive the required amount of moisture. You don't have to worry about irrigation.
Pollinators for apricot Honey
The only disadvantage of this variety is its self-sterility. This means that the plant needs pollinators to set fruit. For this purpose, other varieties of apricots are planted near Medovoy: Kichiginsky, Chelyabinsky, Pikanny, Sibiryak Baikalova, Sayansky, Khabarovsky, Northern Lights, Amur, Gorny Abakan and others.
Other crops with the same flowering period are also suitable for pollination. In the garden, a distance of 3-4 m is maintained between trees.
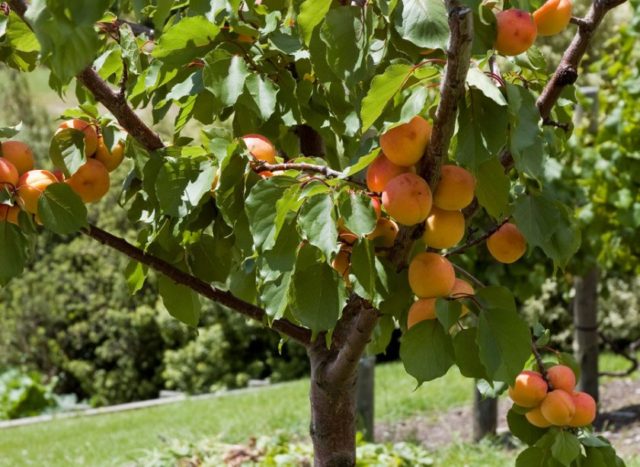

It is better to keep apricot orchards separately from other crops, this will protect them from infection by fungi
Flowering period and ripening time
The fruits ripen in mid-August; the variety is classified as mid-season. Budding begins in early June. Large flowers bloom, which consist of 5-6 white petals. There are yellow stamens in the center. The fruits set by the end of June; before the end of ripening they gain weight and ripen.
Productivity, fruiting
Fruiting begins in the fifth year of vegetation. Until this time, the plant gains green mass. 20-30 kg are harvested from each apricot. This indicator refers to high-yield. Peak fruiting occurs in 7-10 years.
Area of application of fruits
Honey apricots have a pleasant taste and are suitable for fresh consumption. The fruits are good for preparing winter preparations, such as:
- compotes;
- jam;
- jams;
- dried fruits;
- candied fruit;
- canning.
Many gardeners plant this variety for the purpose of preparing winter preparations.
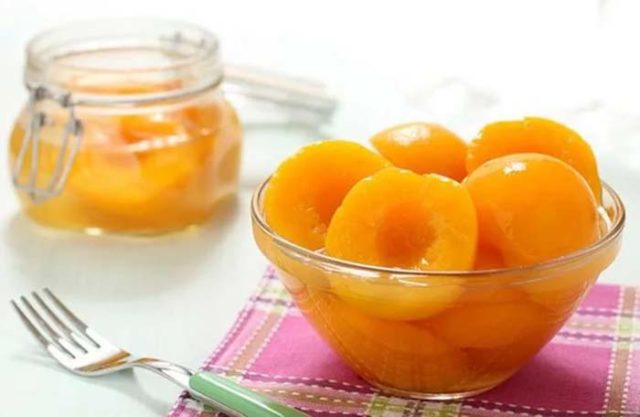

Apricots of the Honey variety are well stored fresh for 4-5 months in a cool place
Resistance to diseases and pests
The Honey apricot variety is resistant to many fungi and pests. However, preventive measures are recommended.To do this, during the flowering period, the plant is treated with fungicides and insecticides. This provides protection against many diseases.
Advantages and disadvantages
Honey apricot has many advantages, which is why gardeners often plant it on their plots. These include:
- mid-ripening;
- drought resistance;
- winter hardiness;
- good taste;
- transportability;
- storage duration;
- resistance to diseases and pests;
- presentable appearance of the fruit.
Among the shortcomings, only self-sterility is noted.
Landing Features
From the photo, honey apricot is similar to its closest relatives, which grow wild in the northern regions. Tree care and planting have their own characteristics.
Recommended timing
Planting work is carried out in early spring or early autumn. In the north, it is recommended to plant seedlings in the spring so that the roots are well established in the soil. Winter planting is suitable for temperate climates and the south.
Choosing a suitable location
Apricot prefers well-lit areas. The plant requires at least 8 hours of sunlight. The tree grows comfortably in gardens, next to fences and bush plantings.

Nurseries sell annual plants; they adapt faster
What crops can and cannot be planted next to apricots?
It is not advisable to plant apple trees, plum trees, pears, peaches, cherries, mountain ash, cherries, currants, raspberries and nuts next to trees. These plants are affected by the same diseases as apricot. They can infect each other. For honey and other varieties, it is better to fence off a separate area in the garden.
Selection and preparation of planting material
It is recommended to buy seedlings from trusted nurseries. Purchasing wood secondhand does not guarantee quality.
When choosing, you should pay attention to the following signs:
- there should be no rot;
- barrel without cuts or scratches;
- dense and healthy foliage;
- healthy roots.
Young seedlings quickly take root.
Landing algorithm
The planting pit begins to be prepared 2-3 weeks before transferring to the ground. Dig a hole 70 cm deep and 80 cm in diameter. The resulting soil is mixed with humus or fertilizer for fruit and berry crops. Cover the hole with half the soil.
Landing algorithm:
- The roots of the seedling are soaked in a solution of potassium permanganate for 24 hours.
- 1 bucket of water is poured into the hole.
- Lower the roots of the tree down and straighten them with your hands.
- Seal the hole layer by layer, pressing each layer with your hands.
- Form a circle around the trunk with a radius of 20 cm and water it generously.
- Cover with mulch to retain moisture.
When planting in spring, the hole can be prepared in the fall, during which time the fertilizers have time to be absorbed into the soil.

If you put fertilizer in the planting hole in advance, it will last for two years.
Subsequent care of the crop
To get a decent harvest of apricots, follow the following rules of care:
- Water the plant 3-4 times per season. A young tree uses 7-8 buckets of water, and an adult tree uses 10. In arid climates, irrigation is increased; in frequent rains, it is limited.
- Fertilizing is combined with watering. Add organic or mineral fertilizers.
- Pruning is carried out three times a year: at the beginning of the season, thinning in the summer and after harvest. Remove all damaged and dry branches.
- Mulch is placed in the tree trunk area; it helps retain moisture and protect against weed growth.
- At the beginning of spring and for the winter, the trunk is whitened until the first branch with a chalk solution.
- During the flowering period, preventive treatments with insecticides and fungicides are carried out.
To avoid infection of apricot with fungi, it is necessary to follow all the rules of agricultural technology. High-quality watering and fertilizing strengthen the health and immunity of the crop.
Diseases and pests
Honey apricot is susceptible to infection by fungal diseases and insect damage when immunity is reduced. This happens during prolonged wet and cool weather.
Types of ailments:
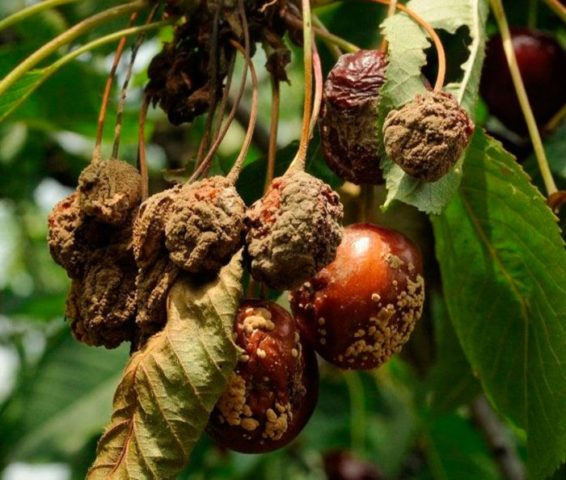
- Moniliosis. The tree begins to slowly dry out, shedding its leaves and fruits. You can fight it with Teldor solution.
The areas affected by moniliosis are clearly visible, they are localized in one place
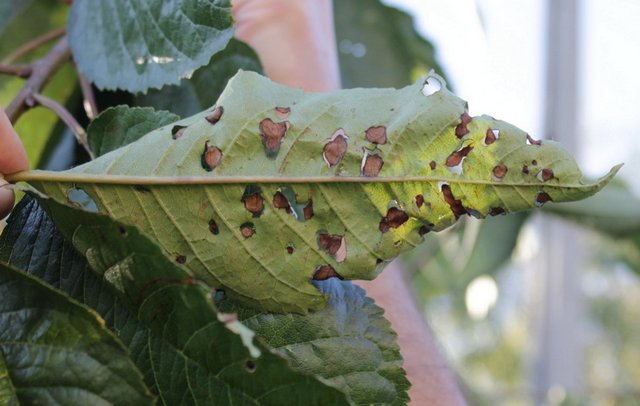
- Hole spot. Spots with a halo appear on the plant’s foliage, the inside dries out and falls off, and holes form. The tree does not receive the necessary nutrition. Treatment is carried out with Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate.
At the initial stage, perforation is similar to sunburn
- Mushroom Valsa. Convex large growths of orange color appear on the leaves of the Honey apricot. A fungicidal spray helps get rid of it.
Do not cut the growths with scissors, this will promote further spread
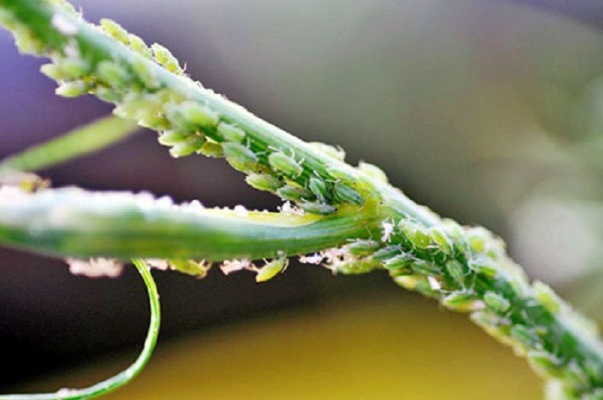
- Green aphid. These are small insects that feed on the leaves of the plant; their bites leave holes. Aphids multiply quickly and can be controlled with an insecticide.
Aphids are very small and difficult to notice in a timely manner.
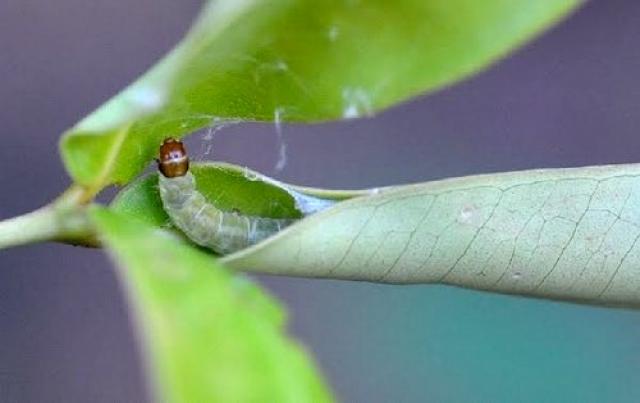
- codling moth. Insects lay larvae inside the Honey apricot bud. After the fruit is formed, they penetrate the apricot and eat it from the inside.
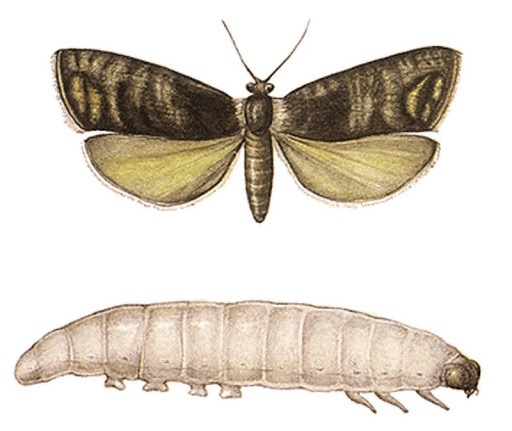
Codling moth butterflies lay larvae during the flowering period; they can be repelled with insecticides
- leaf roller. Caterpillars that suck the juice from the leaves of the Honey apricot, after which it curls and turns yellow.
Leaf rollers can cause serious damage to a healthy Honey apricot tree, after which it will be difficult to restore it
Conclusion
Apricot Honey is distinguished by its winter hardiness. The fruits of the tree have a pleasant and sweet taste, which is why they got their name. Seedlings are sold in nurseries and easily take root in new areas. Productivity is high, fruits can be eaten fresh and processed for the winter.
Reviews of Honey apricot variety