Content
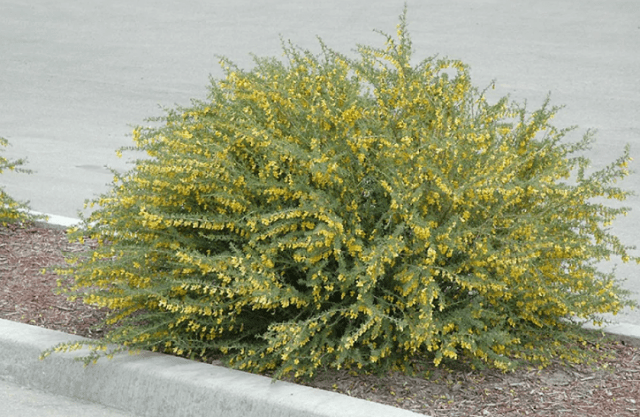
Yellow acacia is an ornamental shrub popular among Russian amateur gardeners. It is valued for its original appearance, bright flowering, honey-bearing and healing properties. In addition, the bush grows quickly, reproduces easily, and does not make any special demands on the planting site or agricultural technology. Therefore, it can be recommended even to not particularly experienced gardeners.
What does yellow acacia look like?
Yellow acacia (also called Caragana Tree) is a deciduous shrub, one of the many representatives of the Caragana genus. Yellow acacia belongs to the legume family. The plant has been “domesticated” for quite a long time – since the mid-50s of the 18th century.
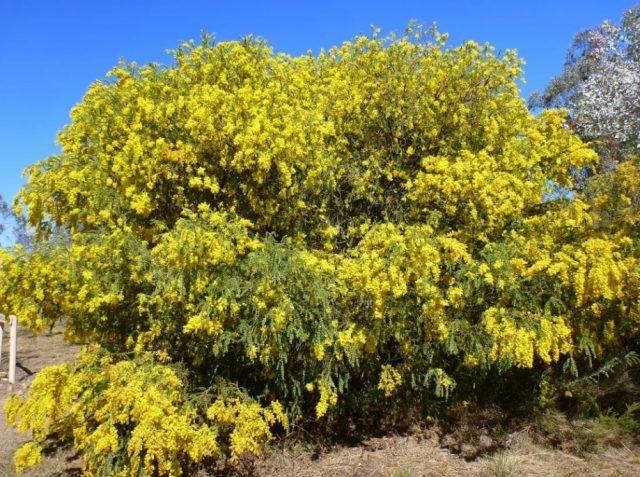

Yellow acacia remains decorative for about 50 years
The plant is a spreading bush with numerous trunks with a diameter of 10-15 cm or a fairly neat tree 2-7 m high. The crown is “weeping”, reaching 2-2.5 m in girth. Hollows often form in the oldest trunks.
The root system of yellow acacia is actively developing both in depth and in breadth. Like other legumes, the roots contain “nodules” with bacteria that “fix” nitrogen in the soil. Accordingly, the “neighborhood” with yellow acacia accelerates the growth of other crops.
The leaves of yellow acacia are medium-sized (4-5 cm), on fairly long petioles, and are located alternately on the branches. Their configuration is complex, each leaf consists of 5-8 pairs of opposite small leaf plates.
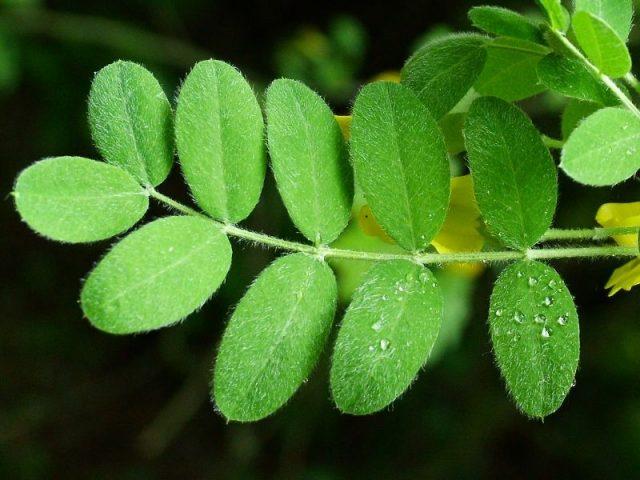

The leaves of the plant are elongated oval or ovoid, sometimes with a pointed tip.
One of the most important characteristics of yellow acacia is its ability to resist any negative external influences. It is wind, heat, drought, smoke and gas resistant. Therefore, plants are actively used for landscaping urban areas, including in large cities. They are also very useful for strengthening slopes and creating wind protection. In terms of cold resistance, the crop belongs to USDA zone 2; it can survive frosts down to -40-45 °C without damage.
Where does yellow acacia grow?
Its habitat includes almost the entire Northern Hemisphere - from Europe to the Far East. In North America it is less common, but it cannot be called a unique plant in the United States and Canada.
Yellow acacia spreads most quickly on sandy and pebble river banks and forest edges. In general, it takes root well on almost bare stones and cliffs, as evidenced by the dense thickets in the Altai, Caucasus, and Sayan Mountains.
When does yellow acacia bloom?
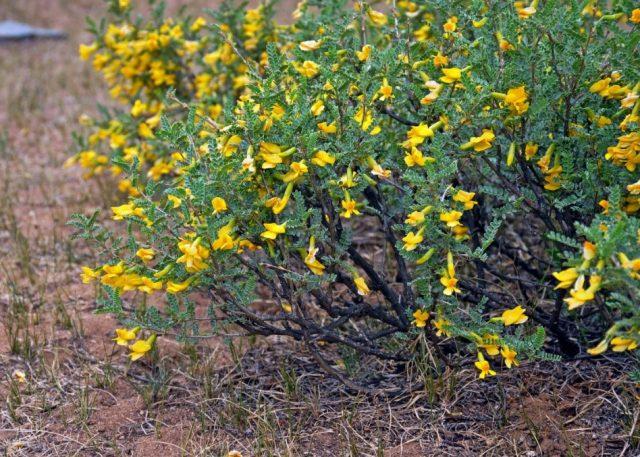
The flowers are axillary, collected in bunch-shaped inflorescences of 3-5 pieces.Like other legumes, they are bisexual, with fused stamens, and belong to the moth type. The corolla is bright yellow, flowering is very abundant.
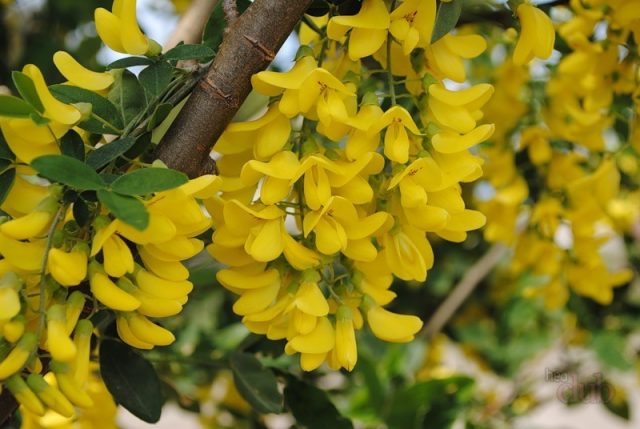

About 300 buds bloom on the bush per day
The flowering period of yellow acacia is 12-15 days. The buds begin to open, depending on the climate in the region, from mid-May to the end of the first ten days of June. Then, in July-August, plants older than 4-5 years ripen fruits in the form of beans with seeds - small “peas”.
Types of yellow acacia
Natural “mutations” of yellow acacia are a fairly common phenomenon. Many of them are very different from the “original”:
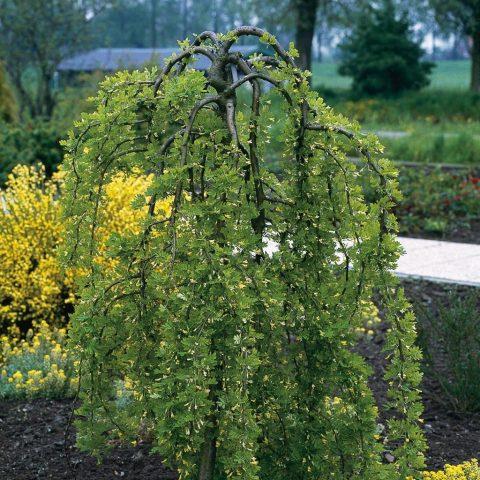
- Crying. A bush with a height and diameter of no more than 2 m. The branches are thin and long, the crown is very similar in configuration to a willow.
Weeping yellow acacia looks impressive as a hedge
- Ussuriyskaya. A dwarf bush with a very dense crown no more than 50 cm high. The shoots are densely strewn with thorns. The flowers are quite large, about 2 cm.
As they wither, the flowers of the Ussuri yellow acacia change color to red.
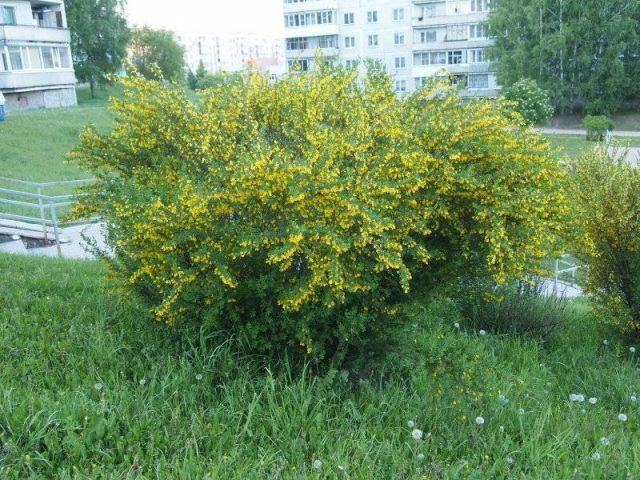
- Shrub. A fairly dense bush with a diameter of 1.5-2 m. The leaves are shaped very much like clover. The flowers are large, golden yellow, solitary.
The bushy yellow acacia shoots are covered with a few, but sharp and long (5-6 cm) thorns
- Dwarf. Depending on the local climate, its height varies between 30-150 cm. Flowering lasts from May-June until the end of August.
Dwarf yellow acacia differs from other varieties in its slow growth rate
Planting yellow acacia
In relation to the soil, yellow acacia is categorically not satisfied with only a “heavy” clayey and highly acidified substrate. It successfully adapts even to very “poor” soil and can tolerate even alkaline and slightly saline soil.
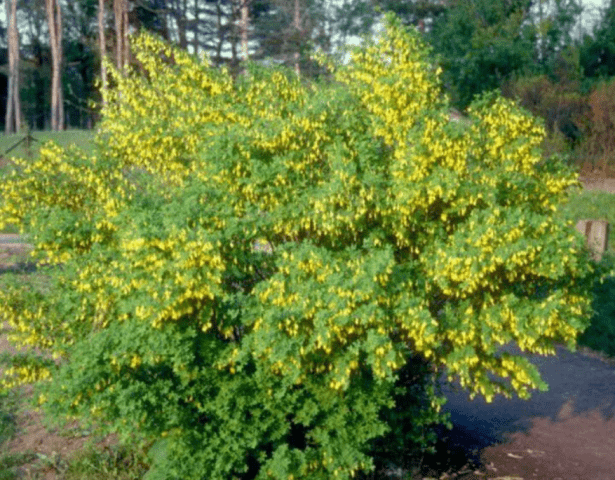

The crop does not suffer from direct sunlight; in the shade the bush will not die either, but it will grow quite slowly and bloom sparingly
When forming a hedge of yellow acacia, 50-70 cm are left between seedlings. In “solo” plantings, the minimum distance to any obstacle is 3 m.
Features of care
When growing yellow acacia, it is enough to limit yourself to a minimum of agrotechnical measures:
- Watering. If there is no rain and it is hot outside, the substrate is moistened weekly, spending 10-15 liters of water per bush.
- Feeding. Mature bushes can easily do without fertilizers, but it is recommended to apply a complex product for ornamental garden perennials at the beginning and end of the season.
- Trimming. It is carried out starting from 2 years of age. Sanitary pruning is required at the beginning and end of the season. Crown formation is best done in the spring. Starting from the age of 8-10 years, anti-aging pruning is practiced, removing 2-3 of the oldest branches every year.
- Shelter for the winter. It is carried out only in the first season for plants planted in autumn. It is enough to pour a mound of mulch 10-15 cm high at the base and wrap the above-ground part with covering material in 2-3 layers.

The crop tolerates drought easily; waterlogging is much worse for it.
How to propagate yellow acacia
It's easy to get new copies. Both the generative method and vegetative methods give equally good results.
Seeds
They can be planted either immediately (in October) or next spring (in March-April). In the first case, their preparation is limited to soaking in water or a biostimulant solution for 8-12 hours, in the second, stratification is required, simulating natural wintering in the soil.
Growing seedlings from yellow acacia seeds is rarely practiced; they are usually sown directly into well-moistened soil, deepened by 4-5 cm. Shoots appear 20-30 days after planting. If the seeds were sown in the spring, the seedlings are transferred to a permanent place in the fall of the same year. After autumn sowing - a year later.

Yellow locust seeds are harvested when the pods containing them are completely dry and cracked.
Dividing the bush
Dividing the bush is the most unpopular propagation method, especially if it is a rare variety. There is always a risk of losing a single copy after the procedure, rather than getting several new ones.
The bush is carefully dug in and “turned” out of the soil, trying, if possible, to preserve the lump of soil and not damage the roots. Then it is divided into 2-4 parts, cutting with a sharp, disinfected knife or pruning shears. New specimens are immediately transplanted to the chosen location.
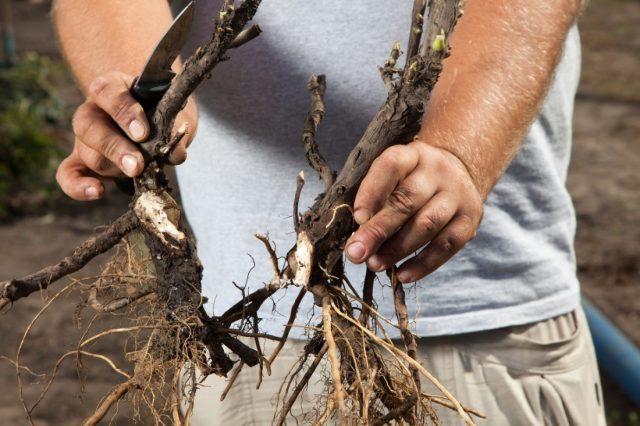

Only completely healthy plants aged 4-8 years are suitable for division.
Cuttings
Planting material for propagating yellow acacia by cuttings - shoot tips 12-15 cm long with 3-4 leaf buds - is formed in abundance after pruning. The lower sections of the cuttings are soaked for several hours in a solution of any root formation stimulator, then they are planted in damp sand, perlite, vermiculite, or other substrate that retains water well. If you provide the “greenhouse effect” and long (10-12 hours) daylight hours, the roots of yellow acacia cuttings will appear in 4-5 weeks.
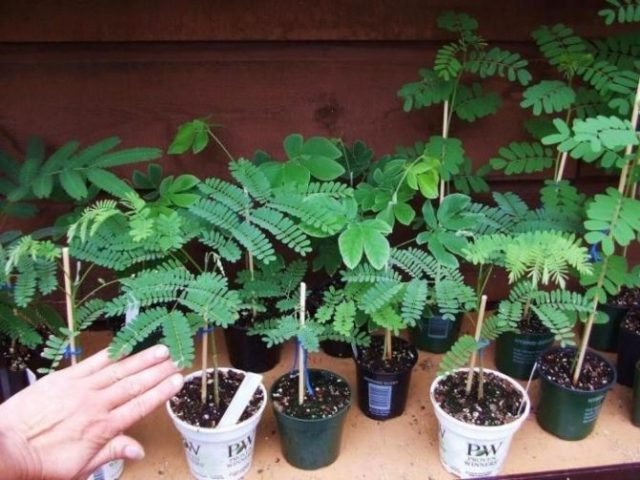

New plants can be planted in a permanent location in the fall or spring, depending on when the cuttings were taken
By layering
Flexible, fairly thin shoots of yellow acacia are easy to bend into the ground without breaking. The middle of the branch is fixed in this position with a wooden “bracket” or a piece of wire, and humus is poured on top with a mound 15-20 cm high.
They do this at the end of spring. During the summer, the rooting site is regularly watered, alternating regular water and fertilizer solutions.
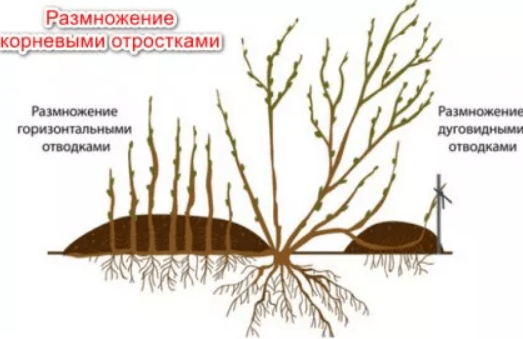
A new seedling appears in August and is transferred to the chosen location in the spring or autumn of next year.
Diseases and pests
The ability of yellow acacia to resist negative external influences includes its resistance to infection by pathogenic microflora and insect attacks. However, neither the “natural” variety nor the varieties bred by breeders have “innate” immunity. Therefore, if a gardener completely neglects caring for a tree, it may well suffer from diseases and pests.
Another risk factor is the formation of a hedge from yellow acacia. Here, dense planting is inevitable, which ensures the lack of normal aeration, uniform illumination and high humidity. And these are very favorable conditions for the development of many pathogenic fungi and pests.
Gardeners most often note signs of yellow acacia infection:
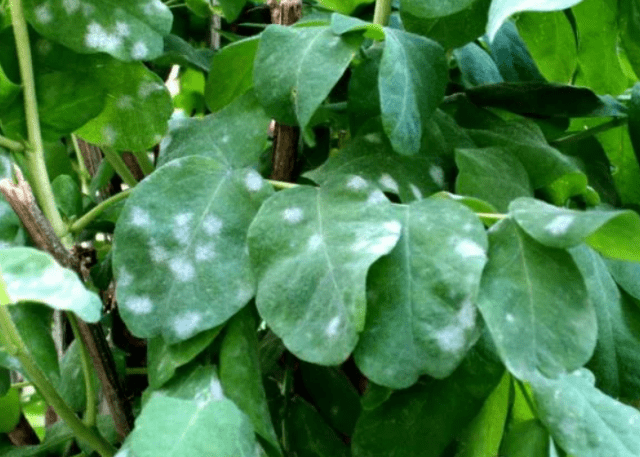
- Powdery mildew. The main symptom is a pale gray or whitish coating, similar to fine powder scattered on the leaves and shoots.
Powdery mildew is a disease from which not a single garden crop, neither ornamental nor fruit-bearing, is immune.
- Rust. On the underside of the leaves, spots of a “fleecy” coating of bright orange-saffron color appear. As
Hot, rainy weather promotes rust development
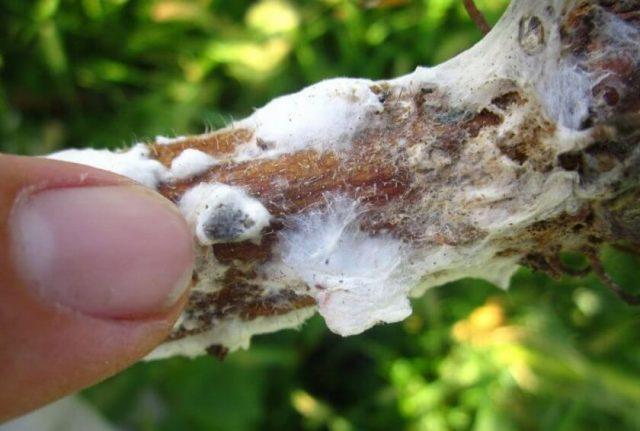
- White rot. Branches and leaves are covered with a rapidly spreading coating, similar to whitish “foam” or “cotton wool”. The tissue underneath turns black and rots.
White rot that often develops on yellow acacia is “accompanied” by a layer of mold that appears on the surface of the soil
Fungicides are used against any fungal diseases on yellow acacia. First you need to cut off all leaves, branches and other parts of the plant that show symptoms of pathogen damage, even minor ones.
The solution is sprayed on the bush itself and the soil underneath it. Its concentration, number of treatments and intervals between them are determined according to the instructions for the selected drug.
Of the pests, yellow acacia is most often attacked by aphids. Colonies of small insects, literally clinging to plants, concentrate mainly on young tissues.
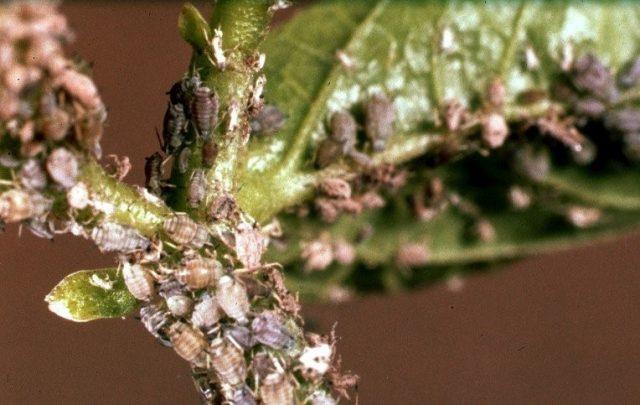

The color of aphids on yellow acacia can be very different - from pale green to black-brown.
Insecticides are used against aphids on yellow acacia.Almost any universal broad-spectrum drug can cope with it, provided the processing algorithm is followed.
Photos in landscape design
Yellow acacia is actively used in landscape design, not only due to its decorative value throughout most of the season, the original shape of the leaves and bright flowering. Among its significant advantages are its rapid growth rate, the ability to easily tolerate even a radical “haircut” and general unpretentiousness.
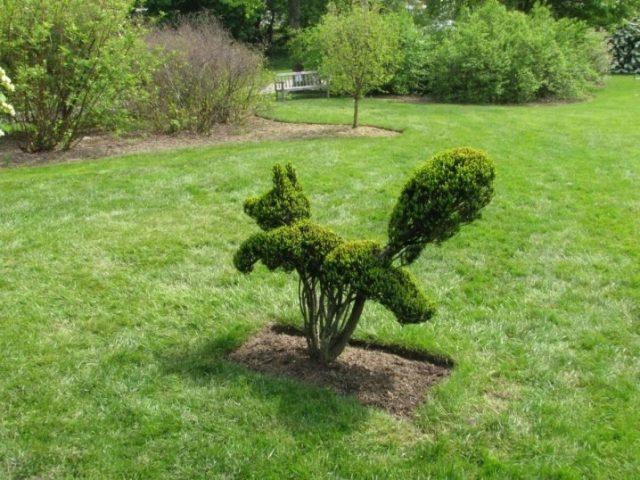

The stems of yellow acacia are flexible and quite thin, so the bush can be given even the most bizarre configuration
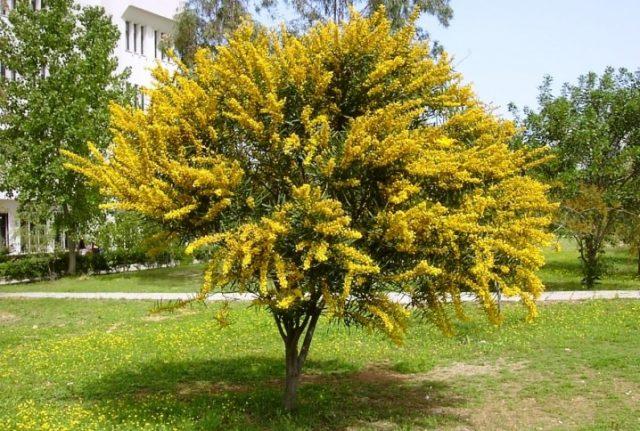

“Solo” planting of yellow acacia is the simplest and most obvious option.
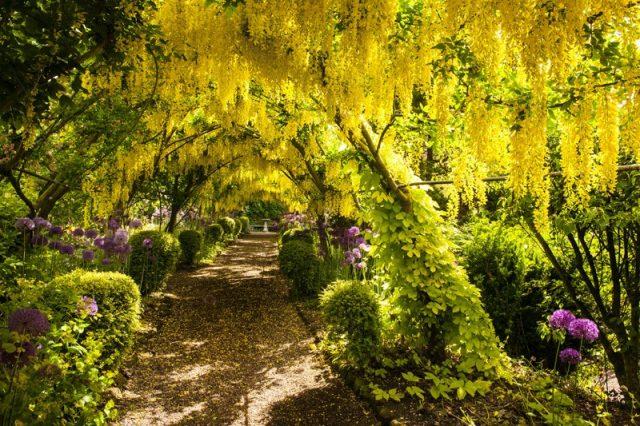

Breeders have developed quite a lot of varieties of yellow acacia with drooping “weeping” shoots - they look more impressive than the “original”

Yellow acacia is resistant to negative external influences, so it is well suited for planting along roads
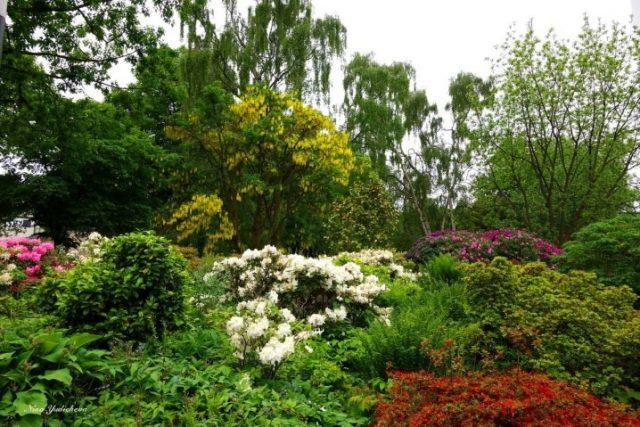

It’s not difficult to choose “companions” for yellow acacia; you just need to take into account its ability to grow quickly
Conclusion
Both the “natural” yellow acacia and its varieties bred by breeders are consistently “in demand” by Russian amateur gardeners. The plant has long been “domesticated”; its advantages and disadvantages are well known. Caring for it will not take much time and effort from the gardener; it does not impose specific requirements on the planting site.
















I recently purchased a garden and am dreaming of a tree-like acacia, from your article I learned about the weeping form!!! complete delight! Just tell me where I can buy a seedling of such beauty?! thank you in advance for your response!!!