Content
The basis of landscape ensembles of gardens and parks located in zones with a temperate climate are frost-resistant, undemanding plants that maintain the effectiveness of the compositions for a long time. The viburnum-leaved vesicle carp Aurea has these characteristics. The yellow crown of this shrub adds color and brightness to the design of garden plots and urban areas.
Description of the bladderwort Aurea
Bladderwort (spirea) is an unpretentious ornamental deciduous shrub belonging to the Rosaceae family. Its homeland is the eastern regions of Asia and North America. Under natural conditions, it grows in valleys and on river banks, in mixed forests.
The Aurea variety of vesicular carp has become popular for landscape design. This shrub, up to 2.5 m high and up to 3–4 m wide, has the following characteristics:
- the brown or brownish bark of the plant peels off in longitudinal stripes with age;
- oblong rounded leaves with 3 - 5 lobes with serrated-toothed edges are unevenly colored yellow: the upper side is a rich shade, the lower side is lighter;
- white flowers are collected in 10 - 15 pcs. into convex corymbose inflorescences;
- small fruits in the form of swollen leaflet bubbles connected to the fruit, burst when pressed.
This description is demonstrated by photos of the viburnum-leaved variety Aurea.
The bladderwort variety Aurea blooms in June-July for 20 - 25 days. The color of its leaves changes during the growing season: when they bloom, they are reddish, in early summer they are yellow. During the flowering of the shrub, the foliage fades, but by the beginning of autumn it again acquires a bright orange hue. Maximum color is achieved in sunny areas. In the shade, the leaves turn dull green.
Over the course of a year, the crop grows by about 0.5 m. It reaches the height of an adult plant in three to four years. The lifespan of the Aurea vesiculus is up to 30 years.
Aurea viburnum in landscape design
Due to its decorative properties and good pliability to cutting, the Aurea variety is used in the design of personal plots, parks, gardens, and public gardens. It is not characterized by bright flowering. This shrub attracts attention more with the color of the leaves and the original shape of the crown.
Some types of landscape design in which the Aurea vesiculus looks impressive:
- Mixborders. The yellow foliage of this plant brightens the background of a shrub group when arranging a one-sided mixborder. If a two-way option is organized, then Aurea is placed as a tapeworm, surrounded by lower representatives of the flora.Important! Mixborder represents a flower garden with free outlines.
The photo shows a version of a mixborder with the Aurea vesicle.
- Contrasting compositions. The color of the shrub expands the possibilities of using contrast in the garden. The light color of Aurea leaves is emphasized by darker coniferous and deciduous plants. It also looks great in combination with red-leaved varieties of bladderwort, such as Diablo or Red Baron.
- Hedges. A trimmed, regular geometrically shaped hedge made of bladderwort is an exquisite decorative element. It fits into modern urban yards where there is no room for large trees. It can be used to fence off a children's or sports ground. Hedges above eye level create a sense of isolation. In gardens and squares they are used to organize U-shaped niches for relaxation.
- Curbs. You can zone the space of an urban area or add splendor and completeness to the decor of a personal plot by forming a border 40 - 60 cm high from bladderwort. Arabesques created from this shrub look attractive.Advice! To make an arabesque (ornamental border flower bed), draw a sketch on graph paper and transfer it to scale to the ground. Shrub seedlings are planted according to the resulting pattern at a distance of 20 - 50 cm. In a year or two they will grow, forming a unique pattern.
- Emphasis on manicured lawns. The plant is placed like a tapeworm on a green area. By periodically pinching its shoots and carefully trimming them, they achieve a smooth shape of the Aurea vesiculus.
Growing conditions for the viburnum leaf variety Aurea
The Aurea variety is unpretentious to the composition of the soil and the sunshine of the area, it is frost-resistant and drought-resistant.In order to fully reveal the varietal characteristics of the plant, the following conditions for its cultivation are recommended:
- Loose, slightly acidic, drained soils that allow oxygen to pass through are preferred;
- close proximity to groundwater and land with a high lime content are undesirable;
- the plant is shade-tolerant, but when choosing a place for planting, preference should be given to open, well-lit areas.
Planting and caring for the Aurea bladderwort
Compliance with planting rules and appropriate care of the Aurea variety will allow you to grow a beautiful plant with bright foliage and protect it from diseases.
Preparing the landing site
The best option for growing the Aurea variety of viburnum-leaved vesicle is medium loam containing a large amount of humus. The nutrient substrate for planting it can be prepared independently using one of the methods:
- mix leaf soil, humus and sand in a 1:1:2 ratio;
- combine turf soil, peat and sand in a ratio of 1:2:2.
Plants for individual compositions are planted in holes. When organizing borders and hedges, trenches are made. They should have a depth and width of 40 - 50 cm. They are prepared two to three weeks before planting and the fertile mixture is poured into them.
Landing rules
In order for the Aurea bladderwrack shrub to take root, you should adhere to the following rules:
- When planting, no fertilizers are added to the soil. A young plant cannot fully absorb them.
- The seedling is placed in the hole together with a lump of earth strictly vertically.
- The hole is covered with earth in portions, compacting each layer.
- After planting, the shrub is well watered.
- If after watering the plant the soil has settled, add soil to the level of the root collar.
- The surface of the hole is mulched with peat or humus.
Watering and fertilizing
Watering and fertilizing are important stages of caring for the Aurea variety. Watering rules:
- During drought and extreme heat, the plant is watered at least 2 times a week.
- Water is poured in small doses under the root.
- Stagnation of water at the roots of the bush should be avoided, otherwise this may lead to powdery mildew infection.
Aurea is fed twice a year:
- in spring - nitrogen-containing fertilizers (urea, ammonium nitrate);
- in the fall - mineral fertilizing, for example, nitroammophoska (1 matchbox per bucket of water).
Trimming
Aurea bladderwort tolerates the pruning procedure well. It is cut for the purpose of:
- stimulate active growth of shoots;
- give the crown the required shape;
- do sanitary pruning.
When forming the crown of the Aurea vesiculus, the following pruning methods are used:
- if it is necessary to obtain a powerful, wide shrub with a large number of trunks, then it is pruned at a level of 40 - 50 cm;
- if the plant is given the shape of a fountain, then thin branches are removed, leaving up to five strong shoots, which are cut to a height of 1.5 m.
Preparing for winter
Bladderwort variety Aurea is a frost-resistant shrub. In the middle zone they do not cover it for the winter. Rarely, after severe frosts, the tops of the plant may freeze.
Newly rooted young shoots require special preparation for winter. In autumn, the soil around them is mulched with peat in a layer of 8 cm. Then the plants are covered with spruce branches.
Reproduction
The Aurea variety is propagated by seeds, cuttings, dividing the bush or layering.
- Propagation by seeds. This method is rarely used for bladderworts. Despite the high germination rate, there is a possibility that the varietal characteristics of the plant, for example, the color of the leaves, will not be preserved.
- Cuttings. An effective and fast method of propagation is cuttings. For it, green shoots are used, cut into 10-20 cm pieces, with several growth points. To prepare the cutting, a thick healthy branch is separated from the bush before flowering, the leaves are removed from its lower part, and half is cut off from the upper part. For several hours, the base of the cutting is immersed in a solution of root formation stimulants. Then it is planted in sand or a soil mixture of sand and peat, watered, and covered with polyethylene. Before leaves and shoots appear, the young plant is periodically ventilated and watered. Then the film is removed from the bushes. For the winter they are covered with spruce paws. The soil around them is mulched with peat, leaves or soil. In the spring, the new bladderwort is transplanted to a permanent location.
- Dividing the bush. The disadvantage of this method is the application of significant physical effort and a small number of new plants obtained.Division is carried out in early spring or late autumn. The bush is cut to 60 - 70 cm, then dug up, removing the entire root system from the soil, and the bush is divided into 4 - 6 parts. The cuttings of the bladderwort are immediately transplanted into pre-prepared holes, preventing their rhizomes from drying out. Afterwards, water and mulch the soil. In the first year, new plants are covered for the winter.Attention! The division of the Aurea vesiculus is carried out so that each new plant gets good roots and a long, healthy, powerful branch.
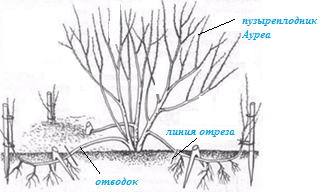
- Reproduction of vesicular carp by layering. The optimal time for this method is the beginning of April, after the first leaves appear. On the vesicular carp of the Aurea variety, a developed shoot directed outward is selected, from which the leaves are removed, leaving a few at the top. A ditch 12-15 cm deep is made under it. Layers are placed in it, without cutting it from the bush, fixed and sprinkled with fertile soil. The tip is not covered with earth. During drought, the shrub is watered abundantly. In autumn, the rooted bladderwort is separated from the parent plant. For the winter it is covered with spruce branches.
Diseases and pests
The varietal feature of Aurea bladderwort is resistance to diseases and pests. In rare cases, with improper care, underfeeding, excessive watering, or improper pruning, the shrub can become affected by chlorosis. A symptom of a plant disease is yellowing of leaves on young shoots and drying out of the apical stems.
Conclusion
Aurea vesica is used to implement landscape solutions of various shapes and purposes. This highly decorative plant will decorate single and group plantings. Shrub seedlings are affordable, take root well, and do not require special care or growing conditions.