Content
Privet is described as a whole genus of shrubs and small trees that grow in Europe, Asia, as well as North Africa and Asia. The photo and description of the privet bush are similar to the lilac known in Russia. This is not surprising - the plants are close relatives. Plantings of this genus are widely used in landscape design. They can easily be given almost any shape, but in an uncut state bush looks very unkempt. Evergreen privet is more popular among landscape design professionals.
Description of privet
This genus includes deciduous and evergreen varieties of shrubs and small trees. More than 50 species of privet are known from descriptions. It is unpretentious in care, grows well in the shade, and therefore has become widespread in landscape design.Most often, the shrub is used as a hedge.
Privet leaves
The description of the leaves of the bush states that they are small in size. The surface is leathery, glossy. The leaves are oval in shape and up to 6 cm long. The shrub, depending on the variety, can shed its leaves during cold periods or remain evergreen. There are also mixed types, when the plant partially sheds its leaves.
Privet flowering
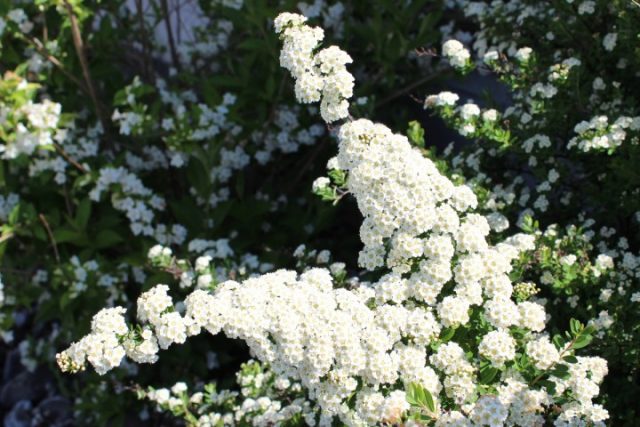
The flowers of the ornamental shrub are white and collected in panicles. The aroma during flowering is strong but pleasant. After flowering, fruits are formed. Flowering begins in early June. If the climate is warm, flowering may begin a week or two earlier. The entire period lasts three months. Blooming privet will always attract attention with its aroma, but in some varieties it is too strong.
During the period when flowers form on the bush, they become especially decorative and pleasant in appearance. The description of the bush compares its flowers with snow covering the branches to the very top.
Privet berries
The fruits are bluish-black. They remain on the bush during the winter. The fruits are popularly known as “wolf berries”. Each berry contains from 1 to 4 seeds, the fruits themselves are round in shape.
Privet height
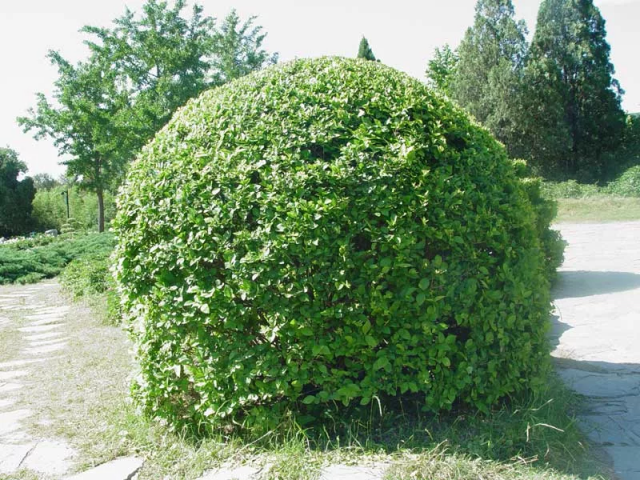
Height from one and a half to three meters, depending on the specific species. There are dwarf varieties that are 60–100 cm in height. The height can be adjusted by pruning. The main advantage of privet is that it can be given absolutely any shape by pruning: a ball, a cone, a pyramid.
Is privet poisonous or not?
The berries and leaves of the bush are considered poisonous. Both people and animals can be poisoned.The berries contain tetroid glycosides, which cause poisoning, especially when consumed in large quantities. At the same time, the bark and some other parts of the bush are used for medicinal purposes. But it is important to know the exact recipe and use it strictly according to the recipe. The fact that privet is poisonous is important to remember for those who have small children in the family, so that decorating the area is not dangerous for them.
The main symptoms of poisoning: colic, weakness, diarrhea. Then there may be loss of coordination of movements and convulsions. In many cases, death is possible.
Privet in landscape design
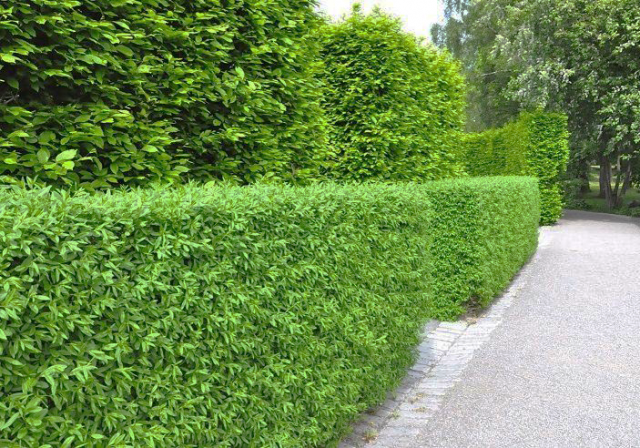
The privet bush is found in many landscape design photos. It is used by both professionals and amateurs to decorate areas. There are many photographs of privet on a trunk, as well as in sculptures. The shrub looks great in single plantings and in group compositions. Its use in hedges is popular. The species variety allows you to select a shrub of a height that will be optimal for the owner of the site. This plant is typically used in topiary, as well as in alpine slides at medium altitudes. Privet as a fence is found everywhere.
Types and varieties of privet
A huge number of varieties allows you to choose your own, suitable decor for every taste. For lovers of evergreen decorations, there are varieties with non-falling leaves, which will please the eye even in winter. Privet types differ in size, spreading crown, length of inflorescences and other parameters.
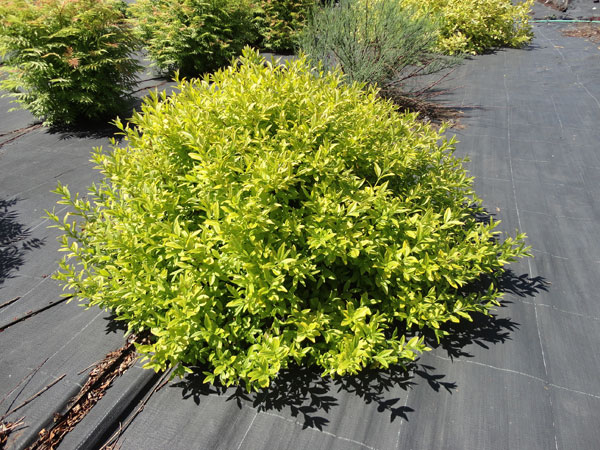
Golden privet
This variety is considered one of the most popular in landscape design. This is a species of Japanese or oval-leaved shrub.The plant is semi-evergreen, that is, the foliage on the bush partially falls off. The leaves are bright in color, the bush looks beautiful even in winter. Grows well in any conditions, does not like wet soil. It loves light, and therefore it is better to choose a lit area with a minimum of shadow. The leaves are glossy, oval in shape, 6 cm long. The leaves have a golden edge along the edges.
The bark is grayish-brown. The berries are black, glossy, poisonous to humans. Golden privet easily tolerates winds, and therefore it is not necessary to plant it on windy slopes.
Privet shiny
Shiny privet grows in China, Korea, and Japan. This shrub has the appearance of a compact tree. The front side of the leaves is glossy, the leaves themselves are 15 cm long. The length of the inflorescences is 18 cm. The shrub blooms for three months. This is one of the most frost-resistant varieties that can easily tolerate frosts of -15 °C. But if the temperature drops further, you will need to cover the shrub so that it survives the too cold winter.
Privet variegated
This is a variety of Chinese privet. A characteristic feature is that the leaves are long, pointed and with golden margins. Yellow-leaved privet produces flowers in the fall. The shrub blooms white with a creamy tint. It has a very pleasant aroma during flowering. But for the first time the shrub will delight you with flowers only 3 years after planting. This variety of privet also likes plenty of sunlight and requires choosing a bright location with minimal shade to plant it. One of the fastest growing varieties of shrubs, reaching a height of two meters. Often used as a hedge.
Japanese Privet
This variety is found naturally in Japan and Korea, hence the name. In Japan it is used for ikebana. Grows up to four meters in height. But in nature it can grow up to 8 meters, but the distinctive feature is that this tree grows slowly. The crown is compact and dense. This shrub can be easily given any shape. Small leaves of dark green color. Japanese privet has high cold resistance parameters, so it grows well in many regions of Russia. The flowers of the Japanese variety are white, but the smell is not very pleasant.
Privet Sinensa
Small shrub, native to China. This is a variety of common privet. In the conditions of central Russia it grows up to two meters, no more, although in a warmer climate this beautiful shrub can grow up to 5 meters. Frost-resistant, as it can withstand short-term frosts down to -30 °C in winter. But Sinensa can withstand such frosts only for a short period. If the winter is too frosty, the bush will have to be covered.
In landscape design, this variety of privet is used as a low hedge, in topiary sculptures, in the form of balls, squares and other shapes.
Privet Argentum
Ligustrum privet variety Argentum is a beautiful plant. It blooms in June-July and grows to about one and a half meters. It tolerates diseases and pests well, and is also easy and beautiful to cut. The shrub got its name from the color of its leaves, which appear to be dusted with white snow.
The variety is drought-resistant and tolerates infrequent watering. Does not like too wet soil.
Privet Atrovirens
This is a common variety of common privet.It blooms from June to July, but the white flowers have too strong a smell. The shrub has straight shoots. This is a semi-evergreen shrub that grows up to 4 meters in height. The leaves are shiny, dark green in color and change to a purple-brown hue in winter. But in spring these leaves fall off. The fruits are black, shiny with several seeds. In general, the plant is considered unpretentious, but shade is not always tolerated well.
Privet Young
This variety is a deciduous shrub. The crown is round in shape up to 5 meters in height. The branches of the bush are thin and curved. The inflorescences are collected in panicles up to 20 cm long. The flowers are white, the aroma is pleasant. The shrub blooms later than other varieties at the very end of summer and beginning of autumn. The fruits are glossy, black-purple, ovoid. Does not like damp, clay soils. Does not tolerate frosty winters well, loves warmth, but is drought-resistant. If it freezes in winter, it usually recovers easily in the spring. It grows quickly and tolerates pruning well.
Planting and care
In order for an ornamental shrub to please the owner’s eye for a long time and decorate the site, it needs to be properly planted and cared for. It is important to choose the optimal planting time and location. The area may depend on the species, but the general conditions of care are almost the same, and there are no huge differences in watering and pruning between different species. Trimming is a mandatory aspect of care, since otherwise the bush will look very sloppy and unkempt.
Landing rules
Garden privet is a cultivated plant, and therefore, when planting, you need to choose and prepare a place. First of all, you need to choose a place. The shrub is not afraid of winds and can grow in the shade.As for the soil, privet is not capricious, but it is better not to grow it on acidic, sandy and dry soils or to add a more nutritious mixture. When choosing a location, you should take into account that the bush should be one meter from the nearest trees or buildings.
It is optimal to prepare the following mixture for planting: 2 parts humus, 3 parts turf, 1 part sand. It is better to plant in the spring, before the buds open. But in the fall, planting privet is also allowed. It is important that it has time to take root before the first frost.
The hole for planting is 65 cm wide and 35 cm deep. More precisely, the depth should be determined by the type of roots of the seedling. The hole should be slightly deeper and wider than the root system. Pour water into the bottom of the dug hole, and then add a layer of crushed stone for drainage. The thickness of the layer is 20 cm. It is better to add nitroammophoska to the prepared nutrient composition and pour a small amount into the hole, preferably in a mound. Place the seedling on top, carefully straightening the roots. Then add the rest of the nutrient mixture.
According to the planting rules, the soil around the seedling should not dry out within 30 days after planting, and then mulch, most often peat, is laid there. Straw can also be used for mulching.
To make a hedge, it is recommended to plant seedlings not in holes, but in trenches. The distance between the bushes is 40 cm. This is the optimal parameter to ensure that the hedge has the required density.
Watering and fertilizing
Most varieties of privet tolerate drought well and do not like waterlogged soil. Therefore, it is not recommended to water the bush too often. If there is enough precipitation in the summer, then watering is not necessary at all.If the summer is dry, then you need to water rarely, but enough. At least three buckets of water should be poured under each bush. Moreover, four such waterings are sufficient per season.
The plant needs feeding in the spring. These must be organic fertilizers. It is enough to add a bucket of humus or compost under each bush. If ornamental trees and privet shrubs are used in hedges, then fertilizers must be distributed under each bush. Superphosphate can be added on top in granular form. Top dressing is sprinkled with earth, and the seedling must be watered.
Loosening and mulching
The top layer of soil must be loosened regularly. This way, air gets better to the roots, and the shrub is less susceptible to diseases, especially those associated with high humidity. Initially, when planting, the soil must be dug well so that it is soft and loose.
Mulching helps retain moisture and protects the plant from frost. Therefore, it is necessary to mulch privet a month after planting and in the fall, before winter frosts.
Trimming
Pruning is the most important aspect of privet care. This ornamental plant is a fast-growing one, and therefore formative pruning is necessary regularly. Unlike many other ornamental shrubs, privet should be pruned right in the year of planting. This first pruning involves cutting off the tips of the shoots.
When the shoots grow 15–20 cm, they are shortened again. This will make the bush more lush. Pruning will be needed during the first two years of the bush's life.
Privet hedges are trimmed twice a year - in May and August.As with all plants, sanitary pruning is important for privet, which is carried out to remove diseased and frostbitten branches. This haircut is carried out in early spring. After removing all diseased branches, the remaining shoots are cut back by another third.
Preparing for winter
Privet easily tolerates relatively warm winters. Some varieties can withstand severe frosts. It is important to prepare the shrub for winter, so that during sanitary pruning you do not have to cut out half the bush in the spring. In preparation for winter, you need to mulch the plant. It is optimal to do this with peat or straw. The layer thickness is 15 cm. As soon as enough snow has fallen, it is recommended to bend the maximum number of branches to the ground and sprinkle them with snow. Under thick snow cover there is a better chance of avoiding freezing of shoots.
Privet propagation
The privet bush reproduces in several ways:
- seeds;
- layering;
- cuttings;
- root suckers.
The most labor-intensive process is considered to be the process of growing decorative privet from a seed. Therefore, propagation by cuttings and layering are more popular methods. But each method has a large number of advantages and disadvantages, so amateur gardeners choose a propagation method to suit their taste. But it’s better to know all the reproduction techniques.
Propagation of privet by cuttings
The most used method because it is simple and accessible. Cuttings taken in summer take root best. Not only young shoots, but also healthy ones from last year are suitable for this. There are practically no problems with them. The optimal length is 10–12 cm. The cuttings are planted for rooting in turf soil with a sandy surface. The cuttings should be planted in the ground at an angle of 45 degrees.It is enough to insert the cuttings 5 cm deep. For high-quality rooting, you will need constant humidity and a temperature of 20–25 °C. To create good conditions, many gardeners use plastic bottles without a neck to cover the cuttings. The very first roots appear within a month, and 90 days after planting the cuttings already have a developed root system. Then the cuttings can be transplanted into larger containers and grown until the height reaches 60 cm. Only after this can the seedlings be safely sent to a permanent place in the garden.
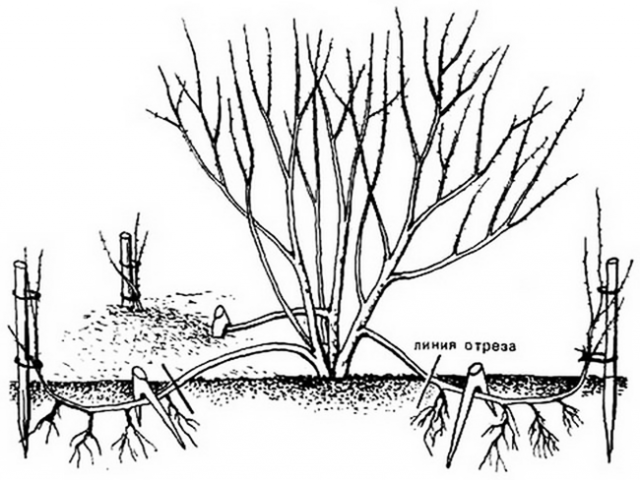
By layering
This is less troublesome than growing cuttings. Almost all varieties of privet can be propagated by layering. The algorithm of actions is simple:
- Choose the strongest branch and bend it to the ground.
- A small cut should be made in the part that will be buried.
- Lock the branch.
- Sprinkle with soil and add sphagnum moss on top.
- Do not bury the top part of the branch.
- Moss should always be kept moist.
If the cuttings take root, the bush branch will grow. This is a sign that rooting was successful. You can separate and plant cuttings of shrubs next spring.
If you don’t want to dig in, then just make a couple of scratches on the branch and place this part in a plastic bag with moistened and nutritious soil. Seal or seal the bag. Using this original method, you can immediately get several cuttings from one bush.
Seeds
It is immediately worth noting that privet seeds have a low germination rate. That is why this method is considered too labor-intensive and costly. But this method also has fans. Seeds can be collected from fruits that appear after 6 years of life of the bush.
To propagate by seeds, it is necessary to select the largest ones and place them in water. Only seeds that will sink should be left for propagation. In the fall, in October, the seeds are placed in the ground so that only the strongest specimens remain in the winter. Exactly in a year the first shoots will appear.
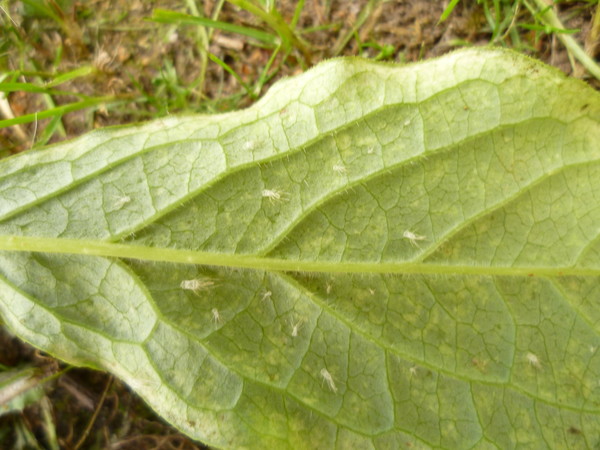
Diseases and pests
Privet and all varieties of shrubs are plants that are not susceptible to virtually any diseases. Among the diseases that are dangerous for shrubs are: powdery mildew, grayish or dark green spotting. Typically, the appearance of such pathologies indicates increased soil acidity. It is enough to treat the plant with special preparations in time and remove diseased shoots.
Pests that often appear on shrubs:
- aphid;
- thrips;
- spider mite;
- scale insect.
To prevent the appearance of pests, it is necessary to treat the bush twice a year with complex pest control preparations.
Conclusion
Photos and descriptions of the privet shrub are known to few people, since this plant is popularly known to everyone as wolfberry. But this is a chic ornamental plant that can decorate any area. Privet is used in the art of bonsai, and Ikebana trees are made from it in Japan. In Europe, in many areas, privet is used to form fences and hedges. But this plant can often be found in single sculptures. It is convenient to cut, it grows quickly, is easy to care for, and is not susceptible to a large number of diseases. That's why he has more and more fans every year.