Content
Rough hydrangea is a plant with beautiful flowers and belongs to the family of the same name. It is of oriental origin and grows wild on the coast of China and Japan. In the 19th century, hydrangea came to Europe, where it immediately fell in love with many garden design lovers.
Description of rough hydrangea
Most species of the Hydrangeaceae family are shrubs up to 3 m high and 2 m wide. Some of its representatives have a tree-like form, in addition, there are also vines among them. Hydrangea bushes have thick branches. They have large inflorescences of a white or lilac hue.
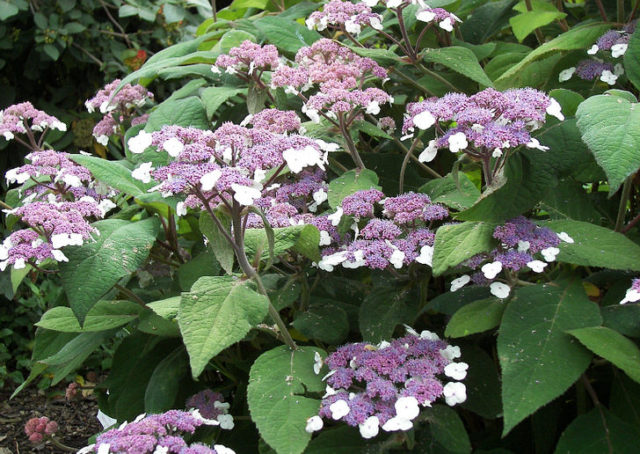

In the middle they consist of many small flowers, around the perimeter they are surrounded by several large white ones with four petals
The leaves can be quite large - up to 35 cm in length and 25 cm in width. Their colors change throughout the season. Young foliage is dark green and velvety. Towards the end of summer it changes color to dark orange.The root system is powerful and branched.
The plant is very hardy: hydrangea can be grown in difficult conditions and at relatively low temperatures. In temperate climates it can be cultivated almost everywhere. Blooms in late summer or early autumn.
Varieties of rough hydrangea
Currently, there are several varieties of rough hydrangea. In addition, constant work is underway to obtain new ones. Below are the most popular varieties of this crop.
Macrophila
The height of this hydrangea is 1.5 m. It has rough leaves covered with small hairs. Their length reaches 35 cm, width - up to 20 cm. The inflorescences are quite large - in some specimens the diameter reaches 20 cm. Hydrangea rough Macrophila is shown in the photo below.
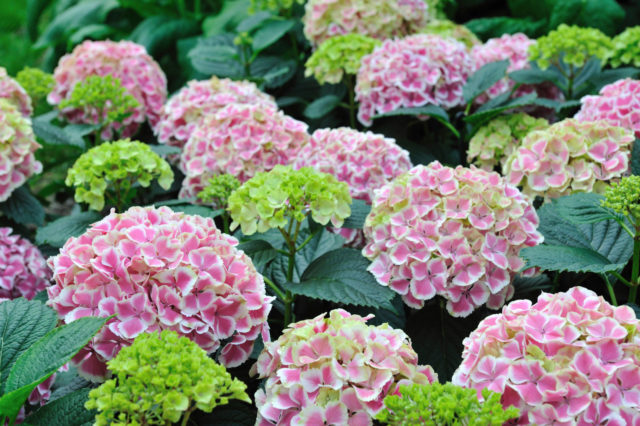

The spherical inflorescences of this variety have a variety of shades; in general, the color of the plant depends on the acidity of the soil
Sargent
The height of the crop can reach 4 m. One of the most popular varieties with velvety leaves. The main feature of this variety is a gradient change in color within one inflorescence and a smooth transition from lilac to pink (and then to blue) over the area of the entire bush. In addition, on some plants the petals may be either white or have a white edge.
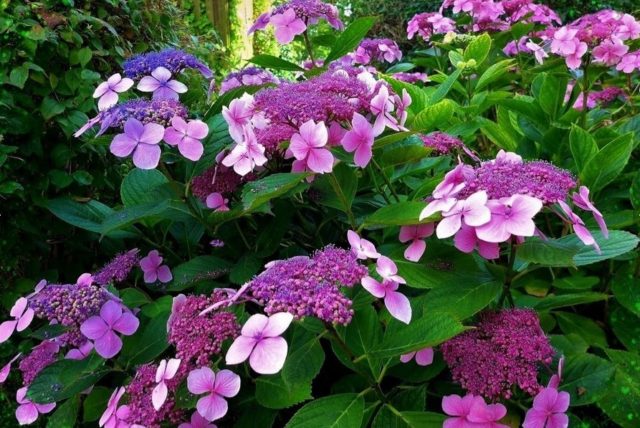

Flowering is quite late and long-lasting, it begins in September and lasts until the first frost.
Hot Chocolate
A variety introduced relatively recently. It has huge inflorescences - up to 30 cm in diameter.
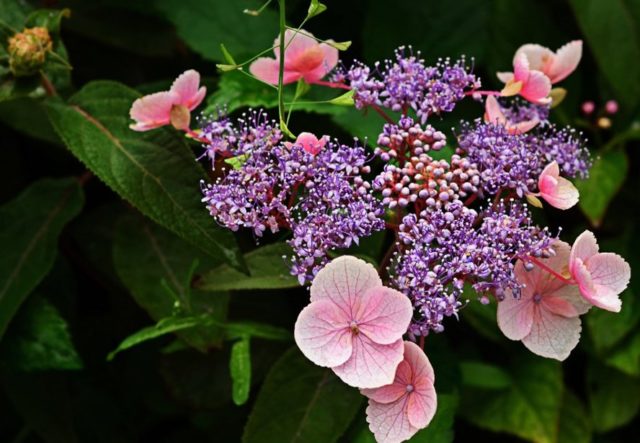

The leaves of this variety also change color, but, unlike the classic change from green to orange, it has a transition from silver to olive
The color of the shoots also changes over time: as the temperature drops, they turn red.
Hydrangea rough in landscape design
Rough hydrangea is widely used in landscape design. Large bushes can be used as a monoculture over large areas. They can be used to create dense hedges and be used as border plants for wide paths.
As a separate design element, rough hydrangea will look beyond any competition, since bright and beautiful flowers attract attention.
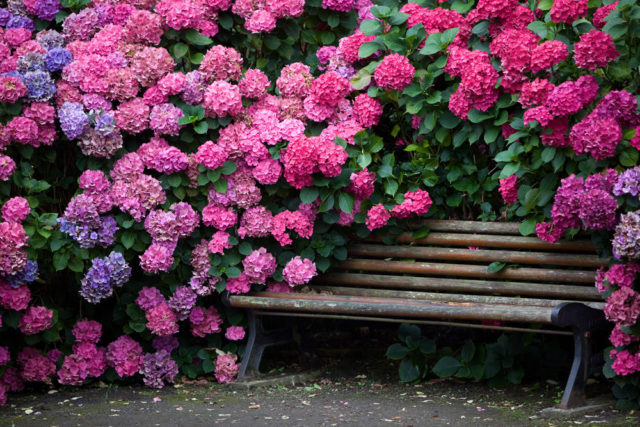
Decorating a bench with the Macrophila variety is a common option for using it in the landscape of a park area.
It is also good to use rough hydrangea as the central element of a large flower bed, surrounded by bushes of bright and large plants, the flowers of which will contrast with it. It looks good surrounded by variegated annuals.
Wintering rough hydrangea
Hydrangea has good winter hardiness, however, in frosts of about -30 ° C, it is recommended to insulate the tree trunk circle to protect the roots of the plant from freezing. You can use fallen tree leaves or sawdust as a covering material.
Planting and caring for rough hydrangea
Planting and caring for rough hydrangea is not particularly difficult. The only thing you should pay close attention to is watering, since the plant needs a lot of moisture.
Selection and preparation of a landing site
The ideal place for rough hydrangea is an area sheltered from the wind in partial shade. The soil must be nutritious and have a pH level of at least 5.0 (slightly acidic).
Preliminary preparation of a site for rough hydrangea consists of clearing it of weeds and applying mineral fertilizers (up to 20 g of superphosphate per 1 sq. m). This must be done two weeks before planting. Usually, it is carried out in the spring.
Before planting, a rough hydrangea seedling should be treated with a growth stimulator by immersing its roots, for example, in Epin's solution. Immediately before installing it in a hole, it is recommended to spray it with a 0.2% solution of potassium permanganate to disinfect it from fungi and pests.
Landing rules
Planting is carried out according to the following scheme:
- Dig a hole 60 cm deep and 70 cm in diameter.
- A drainage layer of coarse crushed stone or broken brick is laid at the bottom.
- Pour 15-20 cm of soil mixture into the hole.
- A seedling is placed in it.
- Sprinkle with soil to the top and tamp lightly.
- Irrigate with 20-30 liters of water.
After planting, the plant is not watered for a week, then the plant goes back to the standard watering schedule.

The first watering of rough hydrangea is carried out immediately after planting.
It is recommended to immediately mulch the bush with a layer of peat 5-10 cm high.
Watering and fertilizing
Rough hydrangea is a moisture-loving crop. Watering is done every 3-4 days. Their norm is from 30 to 50 liters of water per bush. It is advisable to update the mulch layer once every 1-1.5 months.
In the first and second years after planting, rough hydrangea is not fed. Starting from the third year, the following feeding schedule is recommended:
- April – nitrogen mineral fertilizers for increasing green mass (urea).
- June – potassium-phosphorus mineral supplements (superphosphate).
- July - organic matter (rotted manure, compost, chicken manure solution).
- September is a complex fertilizer, including potassium, phosphorus, magnesium and boron.
In the latter case, it is advisable to purchase a specialized feeding mixture for ornamental plants.
Trimming
The plant is not pruned for the first 2-3 years. Subsequently, formative and sanitary treatment of the crown is carried out 2 times a season. The first is performed immediately after the snow melts.
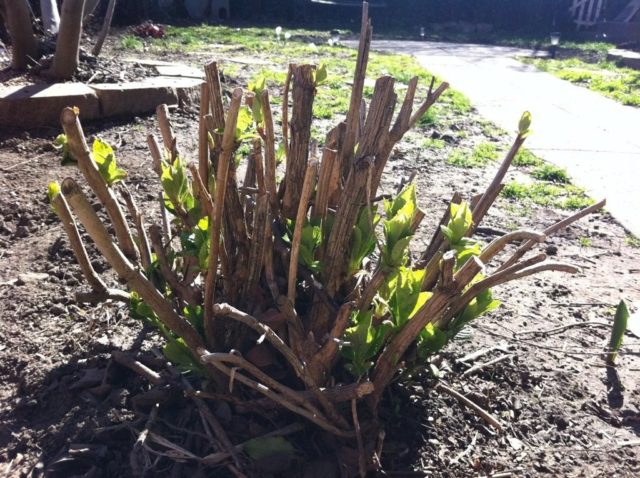

In the spring, in addition to removing shoots that have not overwintered, all last year's shoots are shortened to the lowest bud
Sanitary pruning is performed in the fall. It is part of preparing the plant for winter.
Preparing for winter
At the end of autumn, the plant is sanitary pruned and damaged and too old shoots are removed. After this, moisture-recharging irrigation is done and the tree trunk circle is mulched with a layer of straw, sawdust or fallen leaves up to 20 cm high. In the case of a particularly cold climate, the protective layer is covered with film or agrofibre on top.
Reproduction
Rough hydrangea reproduces in all available ways:
- seeds;
- cuttings;
- layering;
- dividing the bush.
Unlike many ornamental crops, seed propagation of rough hydrangea is used quite often, since plants grown in this way begin to bloom relatively early.
The most effective method of propagation, which provides the maximum amount of planting material, is by cuttings. They are obtained from the side branches.

The length of the cutting must be at least 15 cm, and only one bud is enough
Rooting is carried out in a substrate consisting of peat and sand for a month. The soil must be kept moist.As soon as the cutting reaches a length of 30-40 cm, it is transplanted to a permanent place.
Diseases and pests
The immunity of rough hydrangea is very high. The plant is rarely affected by diseases and pests. If this happens, the cause is most likely to be incorrect agricultural technology.
The most common problem with rough hydrangea is leaf chlorosis. In this case, the color of the plates begins to change to yellow, but the veins always remain green.
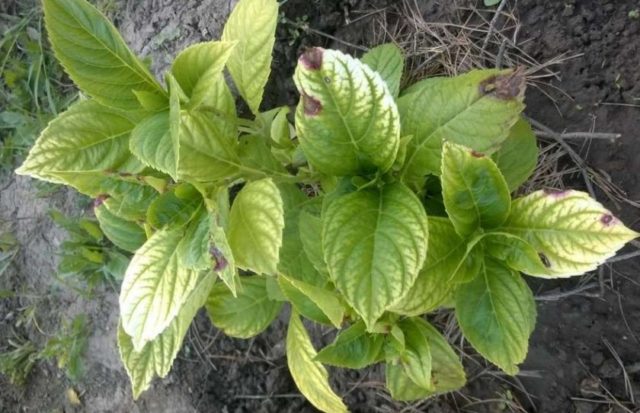

Over time, the leaves become covered with dark brown or brown spots, and later holes appear in their place.
The cause of the disease is iron deficiency. For treatment, damaged areas should be removed, and the remaining parts of the plant should be treated with a 4.5% solution of ferrous sulfate.
In second place in terms of frequency of occurrence is the well-known powdery mildew - a disease caused by fungi of the Erisifaceae family.
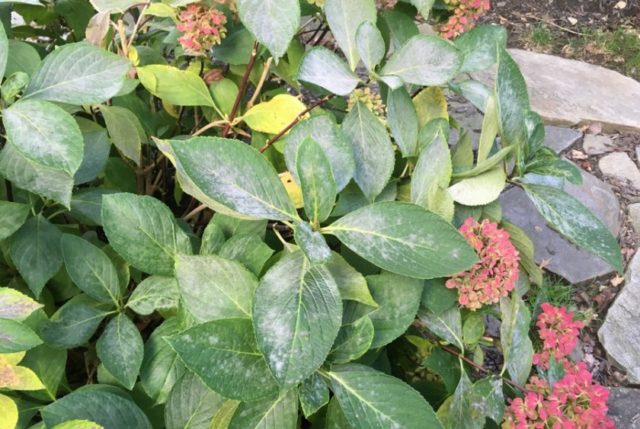

Spots of a pale gray hue appear on the leaves, which darken over time.
To combat powdery mildew, various drugs are used (Bordeaux mixture, copper sulfate, sodium carbonate, etc.), but for rough hydrangea the best remedy is Fundazol. It is used 3-4 times, spraying entire plants at intervals of 1 week.
Of the pests, rough hydrangea is most often attacked by spider mites, a small representative of arthropods that feed on plant sap. It measures less than a millimeter and can sometimes be difficult to detect.
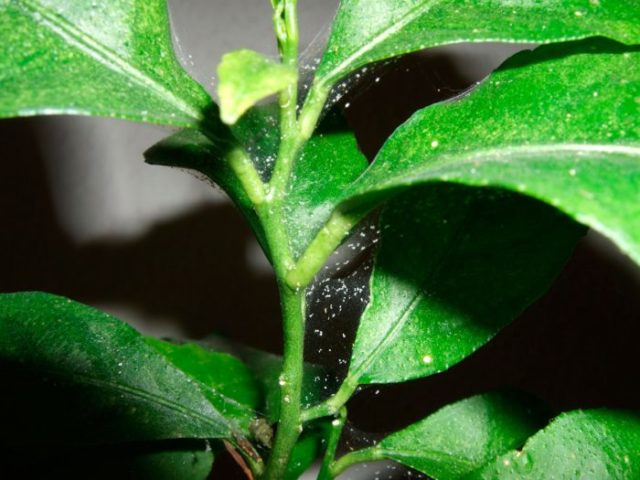

The symptoms of mite infestation are very characteristic - cobwebs with small white dots appear on the lower part of the leaves.
The best remedy against this pest is powerful acaricides: Actellik, Askarin, Iskra.
Conclusion
Rough hydrangea is a beautiful plant with a wide variety of colors and shapes. In addition to the beautiful flowers, the large leaves that change color at the end of the season are also very decorative. The plant is widely used in landscape design.
Reviews of rough hydrangea








