Content
A farmer involved in livestock farming needs to be able to determine the yield of pork meat from live weight in different ways. Its percentage depends on the breed, age, and feeding. The slaughter weight of a pig helps to pre-calculate the farm’s profit, determine the profitability of production, and adjust feeding standards.
Average pig weight at slaughter
The age, breed, and diet of the animal directly affect weight. To determine the time of slaughter, the expected slaughter weight of the pig, the health of the animal and the preparation of a feeding ration, it is necessary to be able to correctly determine the weight of the animal.
Representatives of the Great White breed reach impressive sizes in adulthood: wild boar - 350 kg, pig - 250 kg. The Mirgorod breed is smaller, individuals rarely reach 250 kg.
A Vietnamese boar weighs 150 kg, a pig – 110 kg.
The increase in piglet weight gain depends on the correct composition of the diet, the quality of the feed, and the time of year. The weight of the animal increases in the spring when healthy greens are added to high-calorie feed.The indicator is influenced by the pig’s fatness, which is represented by five categories:
- first – young animals of the bacon type, up to 8 months, weighing 100 kg;
- second – young meat animals, up to 150 kg, gilts – 60 kg;
- third – fatty individuals without age limit with a fat thickness of 4.5 cm;
- fourth – sows and hogs heavier than 150 kg, whose fat thickness is 1.5 – 4 cm;
- fifth – suckling piglets (4 – 8 kg).
Weight gain largely depends on the diet, the addition of vitamins to the pigs’ feed, and the conditions of detention. With a balanced and high-calorie diet, by six months the animal can gain 120 kg. This weight gives a high slaughter yield for pigs.
How much does a boar weigh?
Adult boars weigh more than pigs. The difference is 100 kg. Average values of different breeds of adult boars (in kg):
- Mirgorodskaya - 250, at breeding enterprises - 330;
- Lithuanian white – 300;
- Livenskaya – 300;
- Latvian white – 312;
- Kemerovo - 350;
- Kalikinskaya – 280;
- Landrace - 310;
- Large black – 300 – 350;
- Large white – 280 – 370;
- Duroc - 330 - 370;
- Chervonopoyasnaya - 300 - 340;
- Estonian bacon - 320 - 330;
- Welsh - 290 - 320;
- Siberian Northern - 315 - 360;
- Ukrainian steppe white - 300 - 350;
- North Caucasus - 300 - 350.
Weight of piglets before slaughter
The specific weight of a pig at different ages allows for correction of the quality and quantity of feedings. For all breeds there are average animal weights. Thus, a Large White piglet is much heavier than an Asian herbivore. The weight of piglets, depending on age, has approximate values.
The indicator is influenced by the amount of farrowing of the sow. The more numerous it is, the lighter the piglets.The first month of weight gain depends on the milk production of the pig. From the second month, the quality of nutrition affects the growth of piglets.
Concentrated food promotes rapid weight gain. A diet based on grass, vegetables and fruits slows the rate at which pigs gain weight. When comparing the weight of a piglet with standard values, it is necessary to take into account information about feeding. Increase in piglet weight gain by month (on average, in kg):
- 1st – 11.6;
- 2nd – 24.9;
- 3rd – 43.4;
- 4th – 76.9;
- 5th – 95.4;
- 6th – 113.7.
The error in the mass of Landraces, Large Whites and other breeds that are not fattened before slaughter for more than six months is 10%.
What determines the lethal yield?
After the slaughter of an animal, part of the weight is lost due to evisceration of the carcass, bleeding, separation of legs, skin, and head. The percentage of pork meat yield based on live weight is called slaughter yield. The indicator is influenced by the type of animal, characteristics of the breed, age, fatness, and gender. It is widely used to assess the quality of livestock. The yield of pork from a carcass depends quite critically on the accuracy of measuring live weight. If it is determined incorrectly, the error reaches large values.
Thus, the weight of a pig carcass fluctuates depending on the time of weighing. In the steamed state, it is 2 - 3% heavier than in the cooled state. The body tissues of a young animal contain more moisture than an adult, therefore, the loss of kilograms after slaughter in the first case is more significant.
The change in weight is higher for fatty carcasses than for lean carcasses.
Product yield is affected by:
- diet – fiber results in less weight gain than food with a dense consistency;
- transportation – during delivery to the slaughterhouse, animals become 2% lighter due to stress;
- lack of feeding – before slaughter, 3% of weight is lost in 24 hours without food, as the body spends energy on mobilizing vital functions.
Slaughter yield of pig meat
The slaughter yield for pigs is 70 - 80%. It is equal to the ratio of carcass weight to live weight, expressed as a percentage. The slaughter weight of pigs includes the carcass with the head, skin, fat, without legs, bristles and internal organs, excluding kidneys and kidney fat.
Calculation example:
- With a live weight of a pig of 80 kg, carcass without legs and offal (excluding kidneys) - 56 kg, the slaughter yield is equal to: 56 / 80 = 0.7, which is equal in percentage - 70%;
- With live weight - 100 kg, slaughter weight - 75 kg, the yield is: 75 / 100 = 0.75 = 75%;
- With a live weight of 120 kg and carcass weight of 96 kg, the yield is: 96 / 120 = 0.8 = 80%.
Judging by the indicator, raising pigs is more profitable than raising cattle and sheep. Product yield, compared to other animals, is 25% more. This is possible due to the low bone content. Cattle have 2.5 times more of them than pigs.
The slaughter yield for farmed animals is:
- cattle - 50 - 65%;
- sheep - 45 - 55%;
- rabbits – 60 – 62%;
- poultry - 75 - 85%.
How much does a pork carcass weigh?
In a pig, the yield of meat, lard, and offal depends on the breed, age, and weight of the animal itself.
All bred breeds are divided into three groups:
- Bacon: Pietrain, Duroc, quickly gaining kilograms with a slow build-up of fat and a fast build-up of muscles; have a long body, massive hams;
- Greasy: Hungarian, Mangalitsa, have a wide body, heavy front, meat - 53%, lard - 40%;
- Meat: Livenskaya, Large White - universal breeds.
When the live weight of a pig reaches one hundred kilograms or more, the slaughter yield is 70 - 80%.In addition to meat, the composition includes about 10 kg of bones, 3 kg of waste, 25 kg of lard.
Internal weight
The weight of liver products depends on the age of the pig, its breed, and size. For a 100 kg carcass it is (in kg):
- heart – 0.32;
- lungs – 0.8;
- kidneys – 0.26;
- liver – 1.6.
The percentage of viscera in relation to the total slaughter yield is:
- heart – 0.3%;
- lungs – 0.8%;
- kidneys – 0.26%;
- liver – 1.6%.
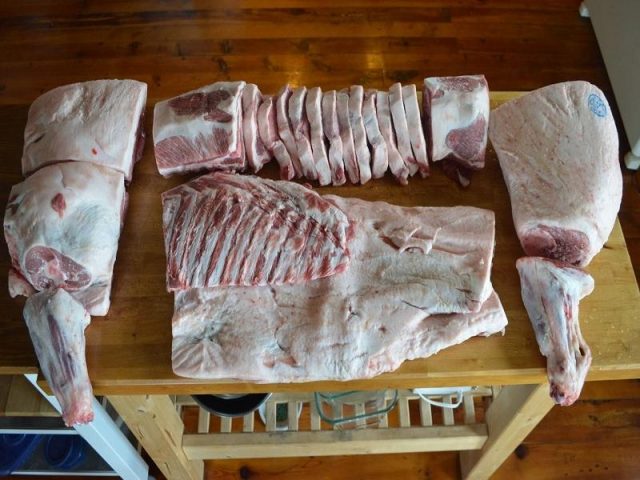
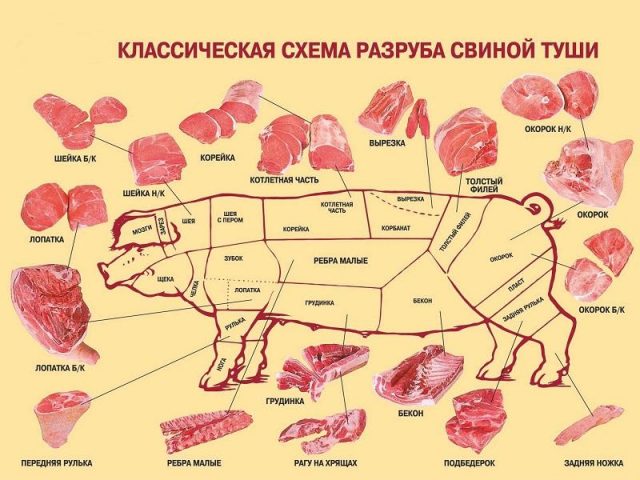
What percentage of meat is in a pig
After slaughter, pig carcasses are divided into half carcasses or quarters. Next, they are divided into cuts, deboning, trimming, and trimming.
Boning is the processing of sides and quarters, in which muscle, fat, and connective tissues are separated from the bones. After it, there is practically no meat on the bones.
The vein is the separation of tendons, films, cartilage, and remaining bones.
On different parts of half carcasses, the yield of pork meat after deboning is of different quality. This is the peculiarity of the procedure. So, when deboning the brisket, back, and shoulders, meat of lower grades is cut off than from other parts. This is due to the large number of veins and cartilage. The trimmer provides, in addition to further cleaning, the final sorting of pork. It is divided into muscle groups, cut longitudinally into kilogram pieces, and the connective tissue is separated from them.
When a carcass is taken to be one hundred percent after slaughter, the yield standards for deboning pork are:
- meat – 71.1 – 62.8%;
- lard – 13.5 – 24.4%;
- bones – 13.9 – 11.6%;
- tendons and cartilage – 0.6 – 0.3%;
- losses – 0.9%.
How much pure meat is in a pig?
Pork is divided into five categories:
- the first is bacon, the animals are specially fattened, there are layers of fat and highly developed muscle tissue;
- the second is meat, it includes carcasses of young animals (40 - 85 kg), the thickness of the bacon is 4 cm;
- third - fatty pork, bacon more than 4 cm;
- fourth – raw materials for industrial processing, carcasses heavier than 90 kg;
- fifth - piglets.
Fourth, fifth categories: pork frozen several times, products obtained from boars are not allowed for sale. The yield of pork cuts to carcass weight is 96%.
The yield of meat, lard and other components from a pig with a live weight of 100 kg is (in kg):
- internal fat – 4.7;
- head – 3.6;
- legs – 1.1;
- meat – 60;
- ears – 0.35;
- trachea – 0.3;
- stomach – 0.4;
- liver – 1.2;
- language – 0.17;
- brains – 0.05;
- heart – 0.24;
- kidneys – 0.2;
- lung – 0.27;
- trim – 1.4.
How much meat is in a 100 kg pig?
When slaughtering pigs that have gained 100 kg, the yield is 75%. Carcasses with a high percentage of bacon are obtained as a result of fattening hybrids of three breeds: Landrace, Duroc, Large White. Bacon meat is rich in muscle tissue and thin bacon. It ripens on the 5th - 7th day after slaughter, when its nutritional value becomes maximum and its properties are optimal for further processing. After 10 - 14 days it is most tender and juicy. The average weight of half carcasses is 39 kg, the backfat has a thickness of 1.5 - 3 cm. The percentage of clean meat yield from a pig carcass is:
- carbonate – 6.9%;
- shoulder blade – 5.7%;
- brisket – 12.4%;
- hip part – 19.4%;
- cervical part – 5.3%.
Conclusion
The yield of pork meat from live weight is quite high - 70 - 80%. There is little waste left after cutting, so the pig is profitable for meat production.Thanks to the many breeds that have been bred, it is possible to select individuals for breeding that are unique in their properties and that meet the market requirements and customer requests. When raising pigs, it is worth constantly monitoring weight gain and, if necessary, adjusting it with feed.